Ion permeation and conduction in a human recombinant 5-HT3 receptor subunit (h5-HT3A)
- PMID: 9508827
- PMCID: PMC2230823
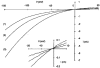
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.653bs.x
Ion permeation and conduction in a human recombinant 5-HT3 receptor subunit (h5-HT3A)
Abstract
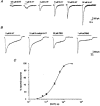
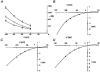
1. A human recombinant homo-oligomeric 5-HT3 receptor (h5-HT3A) expressed in a human embryonic kidney cell line (HEK 293) was characterized using the whole-cell recording configuration of the patch clamp technique. 2. 5-HT evoked transient inward currents (EC50 = 3.4 microM; Hill coefficient = 1.8) that were blocked by the 5-HT3 receptor antagonist ondansetron (IC50 = 103 pM) and by the non-selective agents metoclopramide (IC50 = 69 nM), cocaine (IC50 = 459 nM) and (+)-tubocurarine (IC50 = 2.8 microM). 3. 5-HT-induced currents rectified inwardly and reversed in sign (E5-HT) at a potential of -2.2 mV. N-Methyl-D-glucamine was finitely permeant. Permeability ratios PNa/PCs and PNMDG/PCs were 0.90 and 0.083, respectively. 4. Permeability towards divalent cations was assessed from measurements of E5-HT in media where Ca2+ and Mg2+ replaced Na+. PCa/PCs and PMg/PCs were calculated to be 1.00 and 0.61, respectively. 5. Single channel chord conductance (gamma) estimated from fluctuation analysis of macroscopic currents increased with membrane hyperpolarization from 243 fS at -40 mV to 742 fS at -100 mV. 6. Reducing [Ca2+]o from 2 to 0.1 mM caused an increase in the whole-cell current evoked by 5-HT. A concomitant reduction in [Mg2+]o produced further potentiation. Fluctuation analysis indicates that a voltage-independent augmentation of gamma contributes to this phenomenon. 7. The data indicate that homo-oligomeric receptors composed of h5-HT3A subunits form inwardly rectifying cation-selective ion channels of low conductance that are permeable to Ca2+ and Mg2+.
Figures


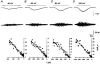
References
-
- Barann M, Göthert M, Bönisch H, Dybek A, Urban BW. 5-HT3 receptors in outside-out membrane patches of N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells: basic properties and effects of pentobarbital. Neuropharmacology. 1997;36:655–664. - PubMed
-
- Belelli D, Balcarek JM, Hope AG, Peters JA, Lambert JJ, Blackburn TP. Cloning and functional expression of a human 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3AS receptor subunit. Molecular Pharmacology. 1995;48:1054–1062. - PubMed
-
- Blandina P, Goldfarb J, Craddock-Royal B, Green JP. Release of endogenous dopamine by stimulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptors in rat striatum. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1989;251:803–809. - PubMed
-
- Brown AM, Hope AG, Peters JA, Lambert JJ. Permeability and single channel conductance of a human recombinant 5-HT3 receptor subunit stably expressed in HEK 293 cells. Journal of Physiology. 1996;495.P:85P.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

