The LysR-type transcriptional regulator CbbR controlling autotrophic CO2 fixation by Xanthobacter flavus is an NADPH sensor
- PMID: 9515907
- PMCID: PMC107038
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.6.1411-1417.1998
The LysR-type transcriptional regulator CbbR controlling autotrophic CO2 fixation by Xanthobacter flavus is an NADPH sensor
Abstract
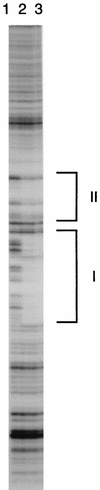
Autotrophic growth of Xanthobacter flavus is dependent on the fixation of carbon dioxide via the Calvin cycle and on the oxidation of simple organic and inorganic compounds to provide the cell with energy. Maximal induction of the cbb and gap-pgk operons encoding enzymes of the Calvin cycle occurs in the absence of multicarbon substrates and the presence of methanol, formate, hydrogen, or thiosulfate. The LysR-type transcriptional regulator CbbR regulates the expression of the cbb and gap-pgk operons, but it is unknown to what cellular signal CbbR responds. In order to study the effects of low-molecular-weight compounds on the DNA-binding characteristics of CbbR, the protein was expressed in Escherichia coli and subsequently purified to homogeneity. CbbR of X. flavus is a dimer of 36-kDa subunits. DNA-binding assays suggested that two CbbR molecules bind to a 51-bp DNA fragment on which two inverted repeats containing the LysR motif are located. The addition of 200 microM NADPH, but not NADH, resulted in a threefold increase in DNA binding. The apparent K(dNADPH) of CbbR was determined to be 75 microM. By using circular permutated DNA fragments, it was shown that CbbR introduces a 64 degree bend in the DNA. The presence of NADPH in the DNA-bending assay resulted in a relaxation of the DNA bend by 9 degree. From the results of these in vitro experiments, we conclude that CbbR responds to NADPH. The in vivo regulation of the cbb and gap-pgk operons may therefore be regulated by the intracellular concentration of NADPH.
Figures



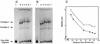
References
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;73:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Croes L M, Meijer W G, Dijkhuizen L. Regulation of methanol oxidation and carbon dioxide fixation in Xanthobacter strain 25a grown in continuous culture. Arch Microbiol. 1991;155:159–163.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

