A conserved histidine is essential for glycerolipid acyltransferase catalysis
- PMID: 9515909
- PMCID: PMC107040
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.6.1425-1430.1998
A conserved histidine is essential for glycerolipid acyltransferase catalysis
Abstract
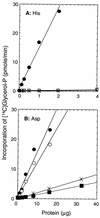
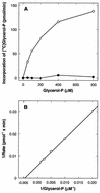
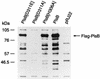
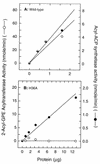
Sequence analysis of membrane-bound glycerolipid acyltransferases revealed that proteins from the bacterial, plant, and animal kingdoms share a highly conserved domain containing invariant histidine and aspartic acid residues separated by four less conserved residues in an HX4D configuration. We investigated the role of the invariant histidine residue in acyltransferase catalysis by site-directed mutagenesis of two representative members of this family, the sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (PlsB) and the bifunctional 2-acyl-glycerophosphoethanolamine acyltransferase/acyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase (Aas) of Escherichia coli. Both the PlsB[H306A] and Aas[H36A] mutants lacked acyltransferase activity. However, the Aas[H36A] mutant retained significant acyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase activity, illustrating that the lack of acyltransferase activity was specifically associated with the H36A substitution. The invariant aspartic acid residue in the HX4D pattern was also important. The substitution of aspartic acid 311 with glutamic acid in PlsB resulted in an enzyme with significantly reduced catalytic activity. Substitution of an alanine at this position eliminated acyltransferase activity; however, the PlsB[D311A] mutant protein did not assemble into the membrane, indicating that aspartic acid 311 is also important for the proper folding and membrane insertion of the acyltransferases. These data are consistent with a mechanism for glycerolipid acyltransferase catalysis where the invariant histidine functions as a general base to deprotonate the hydroxyl moiety of the acyl acceptor.
Figures

References
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Brady L, Brzozowski A M, Derewenda Z S, Dodson E, Dodson G, Tolley S, Turkenburg J P, Christiansen L, Hughe-Jensen B, Norskov L, Thim L, Mensge U. A serine protease triad forms the catalytic centre of a triacylglycerol lipase. Nature (London) 1990;343:767–770. - PubMed
-
- Brown A P, Coleman J, Tommey A M, Watson M D, Slabas A R. Isolation and characterisation of a maize cDNA that complements a 1-acyl sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase mutant of Escherichia coli and encodes a protein which has similarities to other acyltransferases. Plant Mol Biol. 1994;26:211–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

