Comparative in vitro activities and postantibiotic effects of the oxazolidinone compounds eperezolid (PNU-100592) and linezolid (PNU-100766) versus vancomycin against Staphylococcus aureus, coagulase-negative staphylococci, Enterococcus faecalis, and Enterococcus faecium
- PMID: 9517963
- PMCID: PMC105529
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.3.721
Comparative in vitro activities and postantibiotic effects of the oxazolidinone compounds eperezolid (PNU-100592) and linezolid (PNU-100766) versus vancomycin against Staphylococcus aureus, coagulase-negative staphylococci, Enterococcus faecalis, and Enterococcus faecium
Abstract
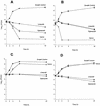
The activities of the oxazolidinone antibacterial agents eperezolid (PNU-100592) and linezolid (PNU-100766) were compared with that of vancomycin against clinical isolates of methicillin-susceptible and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus (n = 200), coagulase-negative staphylococci (n = 100), and vancomycin-susceptible and -resistant Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium (n = 50). Eperezolid and linezolid demonstrated good in vitro inhibitory activity, regardless of methicillin susceptibility for staphylococci (MIC at which 90% of the isolates are inhibited [MIC90] range, 1 to 4 microg/ml) or vancomycin susceptibility for enterococci (MIC90 range, 1 to 4 microg/ml). In time-kill studies, eperezolid and linezolid were bacteriostatic in action. A postantibiotic effect of 0.8+/-0.5 h was demonstrated for both eperezolid and linezolid against S. aureus, S. epidermidis, E. faecalis, and E. faecium.
Figures
References
-
- Brumfitt W, Hamilton-Miller J M T. Antibacterial oxazolidinones. In vitro activity of a new analogue, E3709. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992;15:621–624. - PubMed
-
- Craig W A, Gudmundsson S. Postantibiotic effect. In: Lorian V, editor. Antibiotics in laboratory medicine. 3rd ed. Baltimore, Md: The Williams & Wilkins Co.; 1991. pp. 403–431.
-
- Daly J S, Eliopolous G M, Reiszner E, Moellering R C., Jr Mechanism of action and activity of DuP 105 and DuP 721, new oxazolidinone compounds. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988;21:721–730. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

