Evidence that interleukin-6 is produced in human skeletal muscle during prolonged running
- PMID: 9518745
- PMCID: PMC2230908
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.949bp.x
Evidence that interleukin-6 is produced in human skeletal muscle during prolonged running
Abstract
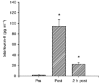
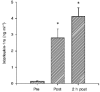
1. This study was performed to test the hypothesis that inflammatory cytokines are produced in skeletal muscle in response to prolonged intense exercise. Muscle biopsies and blood samples were collected from runners before, immediately after, and 2 h after a marathon race. 2. The concentration of interleukin (IL)-6 protein in plasma increased from 1.5 +/- 0.7 to 94.4 +/- 12.6 pg ml-1 immediately post-exercise and to 22.1 +/- 3.8 pg ml-1 2 h post-exercise. IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) protein in plasma increased from 123 +/- 23 to 2795 +/- 551 pg ml-1, and increased further to 4119 +/- 527 pg ml-1 2 h post-exercise. 3. The comparative polymerase chain reaction technique was used to evaluate mRNA for IL-6, IL-1ra, IL-1beta and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha in skeletal muscle and blood mononuclear cells (BMNC) (n = 8). Before exercise, mRNA for IL-6 could not be detected either in muscle or in BMNC, and was only detectable in muscle biopsies (5 out of 8) after exercise. Increased amounts of mRNA for IL-1ra were found in two muscle biopsies and five BMNC samples, and increased amounts of IL-1beta mRNA were found in one muscle and four BMNC samples after exercise. TNF-alpha mRNA was not detected in any samples. 4. This study suggests that exercise-induced destruction of muscle fibres in skeletal muscles may trigger local production of IL-6, which stimulates the production of IL-1ra from circulating BMNC.
Figures
Comment in
-
Skeletal muscle: not simply an organ for locomotion and energy storage.J Physiol. 2009 Feb 1;587(3):509-10. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.165753. Epub 2008 Dec 1. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19047198 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bagby GJ, Crouch LD, Shepherd RE. Exercise and cytokines: Spontaneous and elicited response. In: Hoffman GL, editor. Exercise and Immune Function. New York: CRC Press; 1996. pp. 55–78.
-
- Cannon JG, Evans WJ, Hughes VA, Meredith CN, Dinarello CA. Physiological mechanisms contributing to increased interleukin-1 secretion. Journal of Applied Physiology. 1986;61:1869–1874. - PubMed
-
- Cannon JG, Kluger MJ. Endogenous pyrogen activity in human plasma after exercise. Science. 1983;220:617–619. - PubMed
-
- Cannon JG, Meydani SN, Fielding RA, Fiatarone MA, Meydani M, Farhangmehr M, Orencole SF, Blumberg JB, Evans WJ. Acute phase response in exercise. II. Associations between vitamin E, cytokines, and muscle proteolysis. American Journal of Physiology. 1991;260:R1235–1240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

