Effect of temazepam on oxygen saturation and sleep quality at high altitude: randomised placebo controlled crossover trial
- PMID: 9518909
- PMCID: PMC28461
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.316.7131.587
Effect of temazepam on oxygen saturation and sleep quality at high altitude: randomised placebo controlled crossover trial
Abstract
Objective: To determine the effects of temazepam on the quality of sleep and on oxygen saturation during sleep in subjects at high altitude.
Design: Randomised, blinded, crossover, placebo controlled trial.
Setting: Base camp at Mount Everest (altitude 5300 m).
Subjects: 11 members of British Mount Everest Medical Expedition recently arrived at base camp.
Intervention: Participants were randomly allocated to receive either temazepam 10 mg or placebo on their first night at base camp and the other treatment on the second night.
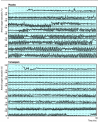
Main outcome measures: Quality of sleep (assessed subjectively), mean arterial oxygen saturation value, and changes in saturation values (as measure of periodic breathing) while participants taking temazepam or placebo.
Results: All participants noted subjective improvements in sleep. Mean saturation value remained unchanged when temazepam was compared with placebo (74.65% v 75.70%, P = 0.5437). There were fewer changes in oxygen saturation when participants took temazepam and when measured as decreases > 4% below the mean value of saturation each hour (P = 0.0036, paired Student's t test (two tailed)).
Conclusions: Participants taking temazepam at 5300 m showed no significant drop in mean oxygen saturation values during sleep. Both the number and severity of changes in saturation during sleep decreased and the quality of sleep improved. This may be a result of a reduction in the number of awakenings and might lead to greater respiratory stability and fewer episodes of periodic breathing. This has the effect of improving the quality of sleep and reducing the number of periods of desaturation during sleep.
Figures
References
-
- Barcroft J. The respiratory function of the blood, part 2. Lessons from high altitude. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1925.
-
- Ravenhill TH. Some experiences of mountain sickness in the Andes. J Trop Med Hyg. 1913;16:313–320.
-
- Anholm JD, Powles AC, Downey R, Houston CS, Sutton JR, Bonnet MH, et al. Operation Everest. II. Arterial oxygen saturation during sleep at extreme altitude. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992;145:817–826. - PubMed
-
- Weil JV. Sleep at high altitude. Clin Chest Med. 1985;6:615–621. - PubMed
-
- Reite M, Jackson D, Cahoon RL, Weil JV. Sleep physiology at high altitude. Electroencephalogr Clin Neuophysiol. 1975;38:463–471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical