Central venous air embolism causing pulmonary oedema mimicking left ventricular failure
- PMID: 9518916
- PMCID: PMC1112636
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.316.7131.604
Central venous air embolism causing pulmonary oedema mimicking left ventricular failure
Figures
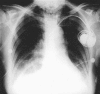

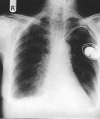
Comment in
-
Temporary pacing before permanent pacing should be avoided unless essential.BMJ. 1998 Jul 4;317(7150):79-80. doi: 10.1136/bmj.317.7150.79a. BMJ. 1998. PMID: 9651288 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kashuk JL, Penn I. Air embolism after central venous catheterisation. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1984;159:249–252. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn M, Fitting JW, Levenberger P. Acute pulmonary edema caused by venous air embolism after removal of a subclavian catheter. Chest. 1987;92:364–365. - PubMed
-
- Clark MC, Flick MR. Permeability pulmonary edema caused by venous air embolism. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984;129:633–635. - PubMed
-
- Okhuda K, Nakahara K, Binder A, Staub NC. Venous air emboli in sheep: reversible increase in lung microvascular permeability. J Appl Physiol. 1981;51:887–894. - PubMed
-
- Flick MR, Perel A, Staub NC. Leukocytes are required for increased lung microvascular permeability after microembolisation in sheep. Circ Res. 1981;48:344–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
