Crystal structure of MTCP-1: implications for role of TCL-1 and MTCP-1 in T cell malignancies
- PMID: 9520380
- PMCID: PMC19850
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.7.3413
Crystal structure of MTCP-1: implications for role of TCL-1 and MTCP-1 in T cell malignancies
Abstract
Two related oncogenes, TCL-1 and MTCP-1, are overexpressed in T cell prolymphocytic leukemias as a result of chromosomal rearrangements that involve the translocation of one T cell receptor gene to either chromosome 14q32 or Xq28. The crystal structure of human recombinant MTCP-1 protein has been determined at 2.0 A resolution by using multiwavelength anomalous dispersion data from selenomethionine-enriched protein and refined to an R factor of 0.21. MTCP-1 folds into a compact eight-stranded beta barrel structure with a short helix between the fourth and fifth strands. The topology is unique. The structure of TCL-1 has been predicted by molecular modeling based on 40% amino acid sequence identity with MTCP-1. The identical residues are clustered inside the barrel and on the surface at one side of the barrel. The overall structure of MTCP-1 superficially resembles the structures of proteins in the lipocalin family and calycin superfamily. These proteins have diverse functions, including transport of retinol, fatty acids, chromophores, pheromones, synthesis of prostaglandin, immune modulation, and cell regulation. However, MTCP-1 differs in the topology of the beta strands. The structural similarity suggests that MTCP-1 and TCL-1 form a unique family of beta barrel proteins that is predicted to bind small hydrophobic ligands and function in cell regulation.
Figures

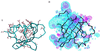
References
-
- Taylor A M R. In: Ataxia telangiectasia: A Cellular and Molecular Link Between Cancer, Neuropathology and Immune Deficiency. Bridges B A, Harnden D G, editors. New York: Wiley; 1982. pp. 53–81.
-
- Stern M H. In: The Causes and Consequences of Chromosomal Aberrations. Kirsch I R, editor. Boca Raton, FL: CRC; 1993. pp. 165–176.
-
- Stern M H, Zhang F, Griscelli C, Thomas G, Aurias A. Hum Genet. 1988;78:33–36. - PubMed
-
- Croce C M. Cell. 1987;49:155–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

