Transcriptional sequencing: A method for DNA sequencing using RNA polymerase
- PMID: 9520387
- PMCID: PMC19857
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.7.3455
Transcriptional sequencing: A method for DNA sequencing using RNA polymerase
Abstract
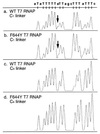
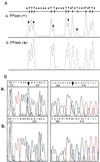
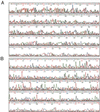
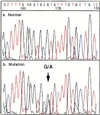
We have developed a sequencing method based on the RNA polymerase chain termination reaction with rhodamine dye attached to 3'-deoxynucleoside triphosphate (3'-dNTP). This method enables us to conduct a rapid isothermal sequencing reaction in <30 min, to reduce the amount of template required, and to do PCR direct sequencing without the elimination of primers and 2'-dNTP, which disturbs the Sanger sequencing reaction. An accurate and longer read length was made possible by newly designed four-color dye-3'-dNTPs and mutated RNA polymerase with an improved incorporation rate of 3'-dNTP. This method should be useful for large-scale sequencing in genome projects and clinical diagnosis.
Figures


References
-
- Huang X C, Quesada M A, Mathies R A. Anal Chem. 1992;64:2149–2154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

