Apoptosis in cord blood T lymphocytes from infants of human immunodeficiency virus-infected mothers
- PMID: 9521148
- PMCID: PMC121363
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.5.2.230-234.1998
Apoptosis in cord blood T lymphocytes from infants of human immunodeficiency virus-infected mothers
Abstract
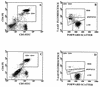
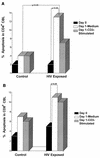
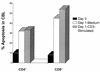
Apoptosis continues to be controversial in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-induced pathogenesis. To investigate whether apoptosis occurs with HIV exposure with or without subsequent infection, levels of apoptosis were measured in cord blood lymphocytes (CBL) from seven newborns delivered to HIV-infected mothers and seven normal, unexposed newborns. Live cells were costained with antibodies to cell surface markers and the DNA dye 7-amino actinomycin D to immunophenotype apoptotic CBL subsets. Apoptosis was measured in fresh and cultured CBL in the presence and absence of CD3 T-cell receptor stimulation. Compared to the CD4+ CBL from HIV-unexposed newborns, CD4+ CBL from six HIV-exposed, noninfected newborns demonstrated significantly greater apoptosis after overnight culture even in the absence of CD3 stimulation. Compared to HIV-unexposed controls, CD8+ CBL from the six HIV-exposed newborns also demonstrated increased levels of apoptosis after overnight culture without stimulation. The one HIV-infected newborn in this study showed the highest levels of CD4+ and CD8+ apoptotic CBL. The data suggest that levels of apoptosis are increased in infants in association with HIV infection. Furthermore, CD4+ and CD8+ cord blood lymphocytes from HIV-exposed infants behaved differently than T lymphocytes from either normal, unexposed infants or an HIV-infected infant. These results suggest that exposure to HIV or HIV-induced factors increases the levels of apoptosis in CBL.
Figures
References
-
- Aggarwal S, Gupta A, Nagata S, Gupta S. Programmed cell death (apoptosis) in cord blood lymphocytes. J Clin Immunol. 1997;17:63–73. - PubMed
-
- Bryson Y J, Pang S, Wei L S, Dickover R, Diagne A, Chen I S Y. Clearance of HIV infection in a perinatally infected infant. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:833–838. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1993 revised classification system for HIV infection surveillance case definition for AIDS among adolescents and adults. Morbid Mortal Weekly Rep. 1993;41(RR-17):1–35. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1994 revised classification system for human immunodeficiency virus infection in children less than 13 years of age. Morbid Mortal Weekly Rep. 1994;43(RR-12):1–10.
-
- Connor E M, Sperling R S, Gelber R, et al. Reduction of maternal-infant transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 with zidovudine treatment. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:1173–1180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

