Alternative gene form discovery and candidate gene selection from gene indexing projects
- PMID: 9521931
- PMCID: PMC310695
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.8.3.276
Alternative gene form discovery and candidate gene selection from gene indexing projects
Abstract
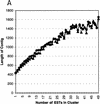
Several efforts are under way to partition single-read expressed sequence tag (EST), as well as full-length transcript data, into large-scale gene indices, where transcripts are in common index classes if and only if they share a common progenitor gene. Accurate gene indexing facilitates gene expression studies, as well as inexpensive and early gene sequence discovery through assembly of ESTs that are derived from genes that have not been sequenced by classical methods. We extend, correct, and enhance the information obtained from index groups by splitting index classes into subclasses based on sequence dissimilarity (diversity). Two applications of this are highlighted in this report. First it is shown that our method can ameliorate the damage that artifacts, such as chimerism, inflict on index integrity. Additionally, we demonstrate how the organization imposed by an effective subpartition can greatly increase the sensitivity of gene expression studies by accounting for the existence and tissue- or pathology-specific regulation of novel gene isoforms and polymorphisms. We apply our subpartitioning treatment to the UniGene gene indexing project to measure a marked increase in information quality and abundance (in terms of assembly length and insertion/deletion error) after treatment and demonstrate cases where new levels of information concerning differential expression of alternate gene forms, such as regulated alternative splicing, are discovered. [Tables 2 and 3 can be viewed in their entirety as Online Supplements at http://www.genome.org.]
Figures







References
-
- Aaronson JS, Eckman B, Blevins RA, Borowski JA, Myerson J, Imran S, Elliston KO. Toward the development of a gene index to the human genome: An assessment of the nature of high-throughput EST sequence data. Genome Res. 1996;6:829–845. - PubMed
-
- Adams MD, Kelley JM, Gocayne JD, Dubnick M, Polymeropoulos MH, Xiao H, Merril CR, Wu A, Olde B, Moreno RF, et al. Complementary DNA sequencing: Expressed sequence tags and human genome project. Science. 1991;252:1651–1656. - PubMed
-
- Adams MD, Dubnick M, Kerlavage AR, Moreno R, Kelley JM, Utterback TR, Nagle JW, Fields C, Venter JC. Sequence identification of 2,375 human brain genes. Nature. 1992;355:632–634. - PubMed
-
- Adams MD, Kerlavage AR, Flieschmann RD, Fuldner RA, Bult CJ, Lee NH, Kirkness EF, Weinstock KG, Gocayne JD, White O, et al. Initial assessment of human gene diversity and expression patterns based upon 83 million nucleotides of cDNA sequence. (Suppl.) Nature. 1995;377:3–17. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
