Protein kinase B activation and lamellipodium formation are independent phosphoinositide 3-kinase-mediated events differentially regulated by endogenous Ras
- PMID: 9528752
- PMCID: PMC121410
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.4.1802
Protein kinase B activation and lamellipodium formation are independent phosphoinositide 3-kinase-mediated events differentially regulated by endogenous Ras
Abstract
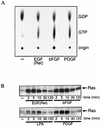
Regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase) can occur by binding of the regulatory p85 subunit to tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins and by binding of the p110 catalytic subunit to activated Ras. However, the way in which these regulatory mechanisms act to regulate PI 3-kinase in vivo is unclear. Here we show that several growth factors (basic fibroblast growth factor [bFGF], platelet-derived growth factor [PDGF], and epidermal growth factor [EGF; to activate an EGF receptor-Ret chimeric receptor]) all activate PI 3-kinase in vivo in the neuroectoderm-derived cell line SKF5. However, these growth factors differ in their ability to activate PI 3-kinase-dependent signaling. PDGF and EGF(Ret) treatment induced PI 3-kinase-dependent lamellipodium formation and protein kinase B (PKB) activation. In contrast, bFGF did not induce lamellipodium formation but activated PKB, albeit to a small extent. PDGF and EGF(Ret) stimulation resulted in binding of p85 to tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins and strong Ras activation. bFGF, however, induced only strong activation of Ras. In addition, while RasAsn17 abolished bFGF activation of PKB, PDGF- and EGF(Ret)-induced PKB activation was only partially inhibited and lamellipodium formation was unaffected. Interestingly, in contrast to activation of only endogenous Ras (bFGF), ectopic expression of activated Ras did result in lamellipodium formation. From this we conclude that, in vivo, p85 and Ras synergize to activate PI 3-kinase and that strong activation of only endogenous Ras exerts a small effect on PI 3-kinase activity, sufficient for PKB activation but not lamellipodium formation. This differential sensitivity to PI 3-kinase activation could be explained by our finding that PKB activation and lamellipodium formation are independent PI 3-kinase-induced events.
Figures






References
-
- Alessi D R, James S R, Downes C P, Holmes A B, Gaffney P R, Reese C B, Cohen P. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase B-alpha. Curr Biol. 1997;7:261–269. - PubMed
-
- Burgering, B. M. T., et al. Unpublished data.
-
- Burgering B M T, Coffer P J. Protein kinase B (c-Akt) in phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signal transduction. Nature. 1995;376:599–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
