NF-kappaB2 is a putative target gene of activated Notch-1 via RBP-Jkappa
- PMID: 9528780
- PMCID: PMC121438
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.4.2077
NF-kappaB2 is a putative target gene of activated Notch-1 via RBP-Jkappa
Abstract
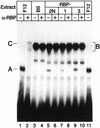
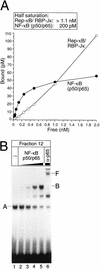
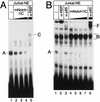
NF-kappaB2 (p100/p52), a member of the NF-kappaB/Rel family of transcription factors, is involved in the regulation of a variety of genes important for immune function. Previously, we have shown that the NF-kappaB2 gene is regulated in a positive and a negative manner. Two kappaB elements within the NF-kappaB2 promoter mediate tumor necrosis factor alpha-inducible transactivation. In addition, we have shown that there exists a transcriptional repression in the absence of NF-kappaB. To identify a DNA binding activity responsible for this transcriptional repression, we have partially purified a nuclear complex, named Rep-kappaB. Here we further analyze this putative repressive binding activity. Detailed examination of Rep-kappaB-DNA interaction revealed the sequence requirements for binding to be almost identical to those of recombination signal binding protein Jkappa (RBP-Jkappa), the mammalian homolog of the protein encoded by Drosophila suppressor of hairless [Su(H)]. In addition, in electromobility shift assays, Rep-kappaB binding activity is recognized by an antibody directed against RBP-Jkappa. By performing transient-transfection assays, we show that human RBP-Jkappa represses basal as well as RelA (p65)-stimulated NF-kappaB2 promoter activity. Studies in Drosophila melanogaster have shown that Su(H) is implicated in the Notch signaling pathway regulating cell fate decisions. In transient-transfection assays we show that truncated Notch-1 strongly induces NF-kappaB2 promoter activity. In summary, our data clearly demonstrate that Rep-kappaB is closely related or identical to RBP-Jkappa. RBP-Jkappa is a strong transcriptional repressor of NF-kappaB2. Moreover, this repression can be overcome by activated Notch-1, suggesting that NF-kappaB2 is a novel putative Notch target gene.
Figures










References
-
- Amakawa R, Jing W, Ozawa K, Matsunami N, Hamaguchi Y, Matsuda F, Kawaichi M, Honjo T. Human Jκ recombination signal binding protein gene (IGKJRB): comparison with its mouse homologue. Genomics. 1993;17:306–315. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Matsuno K, Fortini M E. Notch signaling. Science. 1995;268:225–232. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle P A, Baltimore D. NF-κB: ten years after. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle P A, Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-κB in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin A S., Jr The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:649–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
