Functions of the N- and C-terminal domains of human RAP74 in transcriptional initiation, elongation, and recycling of RNA polymerase II
- PMID: 9528785
- PMCID: PMC121448
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.4.2130
Functions of the N- and C-terminal domains of human RAP74 in transcriptional initiation, elongation, and recycling of RNA polymerase II
Abstract
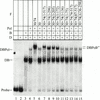
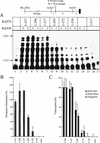
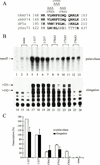
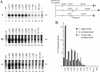
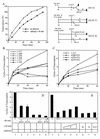
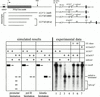
Transcription factor IIF (TFIIF) cooperates with RNA polymerase II (pol II) during multiple stages of the transcription cycle including preinitiation complex assembly, initiation, elongation, and possibly termination and recycling. Human TFIIF appears to be an alpha2beta2 heterotetramer of RNA polymerase II-associating protein 74- and 30-kDa subunits (RAP74 and RAP30). From inspection of its 517-amino-acid (aa) sequence, the RAP74 subunit appears to comprise separate N- and C-terminal domains connected by a flexible loop. In this study, we present functional data that strongly support this model for RAP74 architecture and further show that the N- and C-terminal domains and the central loop of RAP74 have distinct roles during separate phases of the transcription cycle. The N-terminal domain of RAP74 (minimally aa 1 to 172) is sufficient to deliver pol II into a complex formed on the adenovirus major late promoter with the TATA-binding protein, TFIIB, and RAP30. A more complete N-terminal domain fragment (aa 1 to 217) strongly stimulates both accurate initiation and elongation by pol II. The region of RAP74 between aa 172 and 205 and a subregion between aa 170 and 178 are critical for both accurate initiation and elongation, and mutations in these regions have similar effects on initiation and elongation. Based on these observations, RAP74 appears to have similar functions in initiation and elongation. The central region and the C-terminal domain of RAP74 do not contribute strongly to single-round accurate initiation or elongation stimulation but do stimulate multiple-round transcription in an extract system.
Figures
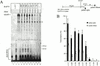

Similar articles
-
The RAP74 subunit of human transcription factor IIF has similar roles in initiation and elongation.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Dec;19(12):8372-82. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.12.8372. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10567562 Free PMC article.
-
Roles for both the RAP30 and RAP74 subunits of transcription factor IIF in transcription initiation and elongation by RNA polymerase II.J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25684-91. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 7929273
-
Dissection of transcription factor TFIIF functional domains required for initiation and elongation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 20;92(13):6042-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.13.6042. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7597077 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase II elongation factors use conserved regulatory mechanisms.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024 Feb;84:102766. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2023.102766. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38181687 Review.
-
DNA wrapping in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II.Biochem Cell Biol. 1999;77(4):257-64. Biochem Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10546889 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CTDP1 and RPB7 stabilize Pol II and permit reinitiation.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 4;16(1):2161. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57513-2. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40038320 Free PMC article.
-
Wrapping of promoter DNA around the RNA polymerase II initiation complex induced by TFIIF.Mol Cell. 1998 Sep;2(3):341-51. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80278-6. Mol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9774972 Free PMC article.
-
Gdown1 Associates Efficiently with RNA Polymerase II after Promoter Clearance and Displaces TFIIF during Transcript Elongation.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 7;11(10):e0163649. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163649. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27716820 Free PMC article.
-
The RAP74 subunit of human transcription factor IIF has similar roles in initiation and elongation.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Dec;19(12):8372-82. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.12.8372. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10567562 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple rounds of transcription by RNA polymerase II at covalently cross-linked templates.Nucleic Acids Res. 1998 Jun 1;26(11):2754-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.11.2754. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998. PMID: 9592165 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arias J, Dynan W S. Promoter-dependent transcription by RNA polymerase II using immobilized enzyme complexes. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:3223–3229. - PubMed
-
- Aso T, Vasavada H A, Kawaguchi T, Germino F J, Ganguly S, Kitajima S, Weissman S M, Yasukochi Y. Characterization of cDNA for the large subunit of the transcription initiation factor TFIIF. Nature. 1992;355:461–464. - PubMed
-
- Bartholomew B, Dahmus M E, Meares C F. RNA contacts subunits IIo and IIc in HeLa RNA polymerase II transcription complexes. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:14226–14231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
