A nuclear matrix protein interacts with the phosphorylated C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II
- PMID: 9528809
- PMCID: PMC121500
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.4.2406
A nuclear matrix protein interacts with the phosphorylated C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II
Abstract
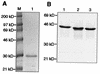
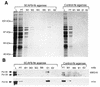
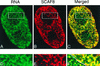
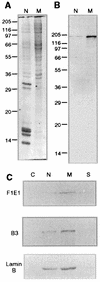
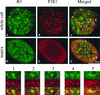
Yeast two-hybrid screening has led to the identification of a family of proteins that interact with the repetitive C-terminal repeat domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II (A. Yuryev et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93:6975-6980, 1996). In addition to serine/arginine-rich SR motifs, the SCAFs (SR-like CTD-associated factors) contain discrete CTD-interacting domains. In this paper, we show that the CTD-interacting domain of SCAF8 specifically binds CTD molecules phosphorylated on serines 2 and 5 of the consensus sequence Tyr1Ser2Pro3Thr4Ser5Pro6Ser7. In addition, we demonstrate that SCAF8 associates with hyperphosphorylated but not with hypophosphorylated RNA polymerase II in vitro and in vivo. This result suggests that SCAF8 is not present in preinitiation complexes but rather associates with elongating RNA polymerase II. Immunolocalization studies show that SCAF8 is present in granular nuclear foci which correspond to sites of active transcription. We also provide evidence that SCAF8 foci are associated with the nuclear matrix. A fraction of these sites overlap with a subset of larger nuclear speckles containing phosphorylated polymerase II. Taken together, our results indicate a possible role for SCAF8 in linking transcription and pre-mRNA processing.
Figures


References
-
- Allison L A, Moyle M, Shales M, Ingles C J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985;42:599–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
