The Italian quality control study for evaluation of CD4 cells in centres involved in the treatment of HIV-1 patients. Italian CD4 Quality Control Group
- PMID: 9528900
- PMCID: PMC1904887
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00520.x
The Italian quality control study for evaluation of CD4 cells in centres involved in the treatment of HIV-1 patients. Italian CD4 Quality Control Group
Abstract
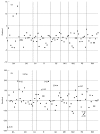
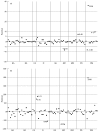
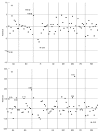
We report on the experience of establishing a national network for a quality control programme in evaluating CD4 cell counts in most Italian centres involved in the care of patients with HIV disease. The 68 centres were divided according to their geographical location into eight groups, and twice a year (tests A and B) they received three coded whole blood samples (two were replicates of the same sample) obtained from two informed HIV+ patients, one with CD4 counts/mm3 expected to be < 200 and one with values > 300. The medians of the determinations performed by the labs involved in each of the eight areas were taken as the 'true' values for each sample. Unsatisfactory performances for percentage of CD4 cells were identified as a CD4 analysis with residual values > or = +/- 5% and with deviates > or = +/- 2. For absolute numbers of CD4 cells, an unsatisfactory performance was defined as CD4 counts with residual > +/- 100 CD4 cells/mm3 and with deviates > or = +/- 2. The residual value is the CD4 value reported by each lab minus the median value. The deviate is the residual divided by the modified interquartile range (IQR x 0.75). Most of the centres provided reliable results. However, some labs failed to provide satisfactory results for percentages (6.25% of the tested labs for test A and 6.17% for test B) or absolute numbers (16.25% test A and 12.34% test B). Only 3.7% of the labs gave unsatisfactory results in both tests. Four of the unsatisfactory results from the two tests gave an error in absolute numbers > +/- 200 CD4 cells/mm3. Our data suggest that most Italian labs provide reliable results in evaluating the numbers of CD4 cells in HIV-1+ samples, but the importance of running a quality control programme is highlighted by our experience with those centres which provide unsatisfactory data which may lead to incorrect classification of the patients or assessment of treatment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The 2005 Italian Quality Control Study for the evaluation of CD4 cells in centers involved in the treatment of HIV type 1 patients.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2007 Jun;23(6):777-81. doi: 10.1089/aid.2006.0295. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2007. PMID: 17604540
-
Predicting the magnitude of short-term CD4+ T-cell recovery in HIV-infected patients during first-line highly active antiretroviral therapy.Antivir Ther. 2010;15(2):165-75. doi: 10.3851/IMP1513. Antivir Ther. 2010. PMID: 20386071 Clinical Trial.
-
External quality assessment program on CD4+ T-lymphocyte counts for persons with HIV/AIDS in Thailand: history and accomplishments.Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2009 Dec;27(4):225-32. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2009. PMID: 20232577
-
Absolute and percent CD4+ T-cell enumeration by flow cytometry using capillary blood.J Immunol Methods. 2011 Sep 30;372(1-2):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2011.07.008. Epub 2011 Jul 20. J Immunol Methods. 2011. PMID: 21787779 Review.
-
Evaluation of a flow cytometry method for CD4 T cell enumeration based on volumetric primary CD4 gating using thermoresistant reagents.J Immunol Methods. 2011 Sep 30;372(1-2):7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2011.07.012. Epub 2011 Jul 29. J Immunol Methods. 2011. PMID: 21835181 Review.
Cited by
-
Adherence to highly active antiretroviral treatment in HIV-infected Rwandan women.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27832. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027832. Epub 2011 Nov 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22114706 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial to the Special Issue "Clinical Immunology in Italy, with Special Emphasis to Primary and Acquired Immunodeficiencies: A Commemorative Issue in Honor of Prof. Fernando Aiuti".Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 30;11(12):3191. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123191. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137412 Free PMC article.
-
A Critical Review on the Standardization and Quality Assessment of Nonfunctional Laboratory Tests Frequently Used to Identify Inborn Errors of Immunity.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 9;12:721289. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.721289. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34858394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD4 immunophenotyping in HIV infection.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008 Nov;6(11 Suppl):S7-15. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1998. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18923413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CCR5 and CXCR4 chemokine receptor expression and beta-chemokine production during early T cell repopulation induced by highly active anti-retroviral therapy.Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Oct;118(1):87-94. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.01033.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10540164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Polk F, Fox R, Brookmeyer R, et al. Predictors of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome developing in a cohort of seropositive homosexual men. New Eng J Med. 1987;316:61–66. - PubMed
-
- Stites DP, Moss AR, Bacchetti P, et al. Lymphocyte subset analysis to predict progression to AIDS in a cohort of homosexual men in San Francisco. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989;52:96–103. - PubMed
-
- Taylor JM, Fahey JL, Detels R, Giorgi JV. CD4 percentage, CD4 number, and CD4:CD8 ratio in HIV infection: which to choose and how to use. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2:114–24. - PubMed
-
- Teitel JM, Freedman JJ, Garvey MB, Kardish M. Two-year evaluation of clinical and laboratory variables of immune function in 117 hemophiliacs seropositive or seronegative for HIV-1. Am J Hematol. 1989;32:262–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

