Endotoxin-neutralizing protein protects against endotoxin-induced endothelial barrier dysfunction
- PMID: 9529059
- PMCID: PMC108066
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.4.1400-1407.1998
Endotoxin-neutralizing protein protects against endotoxin-induced endothelial barrier dysfunction
Abstract
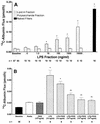
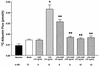
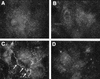
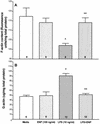
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin, actin reorganization, and opening of the transendothelial paracellular pathway through which macromoles flux. In this study, lipid A was shown to be the bioactive portion of the lipopolysaccharide molecule responsible for changes in endothelial barrier function. We then studied whether endotoxin-neutralizing protein, a recombinant peptide that is derived from Limulus antilipopolysaccharide factor and targets lipid A, could block the effects of lipopolysaccharide on protein tyrosine phosphorylation, actin organization, and movement of 14C-bovine serum albumin across bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cell monolayers. In the presence of serum, a 6-h exposure to lipopolysaccharide (10 ng/ml) increased transendothelial 14C-albumin flux compared to the simultaneous media control. Coadministration of endotoxin-neutralizing protein (> or =10 ng/ml) with lipopolysaccharide (10 ng/ml) protected against lipopolysaccharide-induced barrier dysfunction. This protection was dose dependent, conferring total protection at endotoxin-neutralizing protein/lipopolysaccharide ratios of > or =10:1. Similarly, endotoxin-neutralizing protein was capable of blocking the lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial cell responses that are prerequisite to barrier dysfunction, including tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin and actin depolymerization. Finally, endotoxin-neutralizing protein cross-protected against lipopolysaccharide derived from diverse gram-negative bacteria. Thus, endotoxin-neutralizing protein offers a novel therapeutic intervention for the vascular endothelial dysfunction of gram-negative sepsis and its attendant endotoxemia.
Figures


References
-
- Alpert G, Baldwin G, Thompson C, Wainwright N, Novitsky T J, Gillis Z, Parsonnet J, Fleisher G R, Siber G R. Limulus antilipopolysaccharide factor protects rabbits from meningococcal endotoxin shock. J Infect Dis. 1992;165:494–500. - PubMed
-
- Arditi M, Zhou J, Torres M, Durden D L, Stins M, Kim K S. Lipopolysaccharide stimulates the tyrosine phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase p44, p42, and p41 in vascular endothelial cells in a soluble CD14-dependent manner. Role of protein tyrosine phosphorylation in lipopolysaccharide-induced stimulation of endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1995;155:3994–4003. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman D D, Goldblum S E. Endotoxin induces endothelial barrier dysfunction through protein tyrosine phosphorylation. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:L217–L226. - PubMed
-
- Battafaraono R J, Dahlberg P S, Ratz C A, Johnston J W, Gray B H, Haseman J R, Mayo K H, Dunn D L. Peptide derivatives of three distinct lipopolysaccharide binding proteins inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha secretion in vitro. Surgery. 1995;118:318–324. - PubMed
-
- Brigham K L, Meyrick B. Endotoxin and lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986;133:913–927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

