Reduced virulence of group A streptococcal Tn916 mutants that do not produce streptolysin S
- PMID: 9529097
- PMCID: PMC108104
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.4.1671-1679.1998
Reduced virulence of group A streptococcal Tn916 mutants that do not produce streptolysin S
Abstract
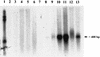
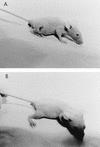
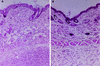
Streptolysin S (SLS) is a potent cytolytic toxin produced by nearly all group A streptococci (GAS). SLS-deficient Tn916 insertional mutants were generated from two clinical isolates of GAS, MGAS166s and T18Ps (M serotypes 1 and 18, respectively), by transposon mutagenesis using Tn916 donor strain Enterococcus faecalis CG110. Representative nonhemolytic transconjugants SBNH5 and SB30-2 each harbored a single Tn916 insertion in identical loci. The insertion in SBNH5 was located in the promoter region of an open reading frame, designated sagA, rendering it transcriptionally inactive. Protease, streptolysin O, and DNase activities and the production of M protein remained the same in the nonhemolytic mutants and the wild-type strains, as did the growth rates and exoprotein profiles. Transconjugants were evaluated in an established murine model by injecting the organisms subcutaneously and monitoring the mice for alterations in weight and the development of necrotic lesions. Animals infected with SBNH5, compared to those infected with MGAS166s, gained weight during the first 24 h (+1.15 versus -1.16 g; P < 0.05) and had fewer necrotic lesions (0 versus 7; P = 0.0007). Animals infected with SB30-2, compared to those infected with T18Ps, also gained weight within the first 24 h (+0.54 versus -0.66 g; P < 0.05) and produced fewer necrotic lesions (1 versus 8; P = 0.001). Revertants of the mutants in which Tn916 had been excised regained the hemolytic phenotype and the virulence profile of the wild-type strains. This study demonstrates that SLS-deficient mutants of GAS, belonging to different M serotypes and containing identical Tn916 mutations, are markedly less virulent than their isogenic parents.
Figures



References
-
- Alouf J E. Streptococcal toxins (streptolysin O, streptolysin S, erythrogenic toxin) Pharmacol Ther. 1980;11:661–717. - PubMed
-
- Barnard W G, Todd E W. Lesions in mouse produced by streptolysins O and S. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1940;51:43–47.
-
- Bernheimer A W. Streptococcal infections. New York, N.Y: Columbia University Press; 1954. p. 19.
-
- Bernheimer A W. Hemolysins of streptococci: characterization and effects on biological membranes. In: Wannamaker L W, Matson J M, editors. Streptococci and streptococcal diseases. New York, N.Y: Academic Press; 1972. pp. 19–31.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

