Characteristics of invasive candidiasis in gamma interferon- and interleukin-4-deficient mice: role of macrophages in host defense against Candida albicans
- PMID: 9529101
- PMCID: PMC108108
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.4.1708-1717.1998
Characteristics of invasive candidiasis in gamma interferon- and interleukin-4-deficient mice: role of macrophages in host defense against Candida albicans
Abstract
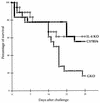
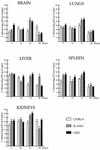
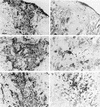
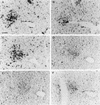
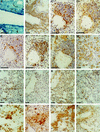
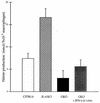
Murine models of invasive candidiasis were used to study the in vivo importance of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and interleukin-4 (IL-4) in host defense against Candida albicans and to characterize the tissue inflammatory reactions, with special reference to macrophages (Mphi). Knockout (KO) IFN-gamma-deficient (GKO) and IL-4-deficient (IL-4 KO) and C57BL/6 parental mouse strains were challenged intraperitoneally with 10(8) C. albicans blastoconidia. Survival of GKO mice was significantly lower (16.7%) than that of C57BL/6 control (55.5%) and IL-4 KO (61.1%) animals, but was not correlated with the extent of organ colonization. Immunohistological analysis with a panel of myeloid and lymphoid markers revealed multiple renal abscesses, myocarditis, hepatitis, meningoencephalitis, and pneumonia in each strain, with a dominant presence of Mphi. In the absence of IFN-gamma, C. albicans induced striking changes in the phenotype of alveolar Mphi and extensive perivascular lymphoid infiltrates in the lung. Impairment in nitric oxide production by peritoneal Mphi was shown only in GKO mice, and they produced Candida-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG), IgM, IgA, and IgG subclasses in lower titers. Our in vivo studies with KO mice elucidate a critical role for IFN-gamma, but not IL-4, in host defense against C. albicans.
Figures
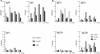
References
-
- Akhiani A A, Lycke N, Nilsson L-Å, Olling S, Ouchterlony Ö. Lack of interferon-γ receptor does not influence the outcome of infection in murine Schistosomiasis mansoni. Scand J Immunol. 1996;43:257–262. - PubMed
-
- Baghian A, Lee K W. Elimination of Candida albicans from kidneys of mice during short-term systemic infections. Kidney Int. 1991;40:400–405. - PubMed
-
- Balish E, Jensen J, Warner T, Brekke J, Leonard B. Mucosal and disseminated candidiasis in gnotobiotic SCID mice. J Med Vet Mycol. 1993;31:143–154. - PubMed
-
- Beck-Sagué C M, Jarvis W R the National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System. Secular trends in the epidemiology of nosocomial fungal infections in the United States, 1980–1990. J Infect Dis. 1993;167:1247–1251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

