Enhancement of lipopolysaccharide-induced neutrophil oxygen radical production by tumor necrosis factor alpha
- PMID: 9529106
- PMCID: PMC108113
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.4.1744-1747.1998
Enhancement of lipopolysaccharide-induced neutrophil oxygen radical production by tumor necrosis factor alpha
Abstract
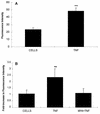
Although tissues become exposed to both exogenous and endogenous cell-activating mediators during infection, there is little appreciation of the effects of subjecting cells to multiple mediators. We examined the hypothesis that the response of neutrophils to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is significantly altered in the presence of the endogenous mediator tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF). The data showed that human neutrophils pretreated with TNF for 10 to 30 min, displayed significantly enhanced superoxide production in response to LPS (from either Escherichia coli K-235 or E. coli O127:B8), measured as lucigenin-dependent chemiluminescence (CL), seen as an increase in the initial peak rate as well as the total CL accumulated over the incubation period. TNF amplified the response to LPS at 1 to 100 U of TNF/10(6) neutrophils and was able to enhance the response to a wide range of concentrations of LPS (0.01 to 1,000 ng/ml). The TNF-induced increase in the LPS response was paralleled by an increase in LPS binding to the neutrophils, which could be abrogated by an anti-CD14 monoclonal antibody. The results demonstrate that TNF significantly increases the LPS-induced release of oxygen radicals in neutrophils through the upregulation of cell surface CD14.
Figures



References
-
- Beutler B, editor. Tumor necrosis factors, the molecules and their emerging role in medicine. New York, N.Y: Raven Press; 1992.
-
- Dziarski R. Cell-bound albumin is the 70-kDa peptidoglycan-, lipopolysaccharide-, and lipoteichoic acid-binding protein on lymphocytes and macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:20431–20436. - PubMed
-
- Ferrante A, Kowanko I, Bates E J. Mechanisms of host tissue damage by cytokine-activated neutrophils. In: Coffey R G, editor. Granulocyte responses to cytokines: basic and clinical research. New York, N.Y: Marcel Dekker, Inc.; 1992. pp. 499–521. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

