Expression of multiple pili by Legionella pneumophila: identification and characterization of a type IV pilin gene and its role in adherence to mammalian and protozoan cells
- PMID: 9529112
- PMCID: PMC108119
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.4.1768-1775.1998
Expression of multiple pili by Legionella pneumophila: identification and characterization of a type IV pilin gene and its role in adherence to mammalian and protozoan cells
Abstract
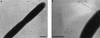
Legionella pneumophila expresses pili of variable lengths, either long (0.8 to 1.5 microm) or short (0.1 to 0.6 microm), that can be observed by transmission electron microscopy. We have identified a gene in L. pneumophila with homology to the type IV pilin genes (pilEL). An insertion mutation was constructed in pilEL and introduced into the L. pneumophila wild-type strain by allelic exchange. The pilin mutant is defective for expression of long pili. Reintroduction of the pilin locus on a cosmid vector restores expression of the long pili. The L. pneumophila pilEL mutant exhibited approximately a 50% decrease in adherence to human epithelial cells (HeLa and WI-26 cells), macrophages (U937 cells), and Acanthamoeba polyphaga but had a wild-type phenotype for intracellular replication within these cells. Southern hybridization analysis showed that the pilEL locus is present in L. pneumophila serogroups 1 through 13 but is variable in 16 other Legionella species. The presence of a type IV pilin gene and its expression by L. pneumophila may provide an advantage for colonization of lung tissues during Legionnaires' disease and invasion of amoebas in the environment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Natural competence for DNA transformation by Legionella pneumophila and its association with expression of type IV pili.J Bacteriol. 1999 Mar;181(5):1395-402. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.5.1395-1402.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10049368 Free PMC article.
-
Type IV pili and type II secretion play a limited role in Legionella pneumophila biofilm colonization and retention.Microbiology (Reading). 2006 Dec;152(Pt 12):3569-3573. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2006/000497-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2006. PMID: 17159209
-
Identification and temperature regulation of Legionella pneumophila genes involved in type IV pilus biogenesis and type II protein secretion.Infect Immun. 1998 Apr;66(4):1776-82. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.4.1776-1782.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9529113 Free PMC article.
-
Invasion of mammalian and protozoan cells by Legionella pneumophila.Subcell Biochem. 2000;33:383-410. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-4580-1_15. Subcell Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10804863 Review. No abstract available.
-
Analysis of virulence factors of Legionella pneumophila.Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1993 Apr;278(2-3):348-58. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80851-0. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1993. PMID: 8347938 Review.
Cited by
-
Pseudomonas stutzeri has two closely related pilA genes (Type IV pilus structural protein) with opposite influences on natural genetic transformation.J Bacteriol. 2001 Apr;183(7):2359-66. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.7.2359-2366.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11244078 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis in macrophages and alveolar epithelial cells during early stages of infection by Legionella pneumophila and its role in cytopathogenicity.Infect Immun. 1999 Feb;67(2):862-70. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.2.862-870.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 9916101 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of macrophage-specific infectivity loci (mil) of Legionella pneumophila that are not required for infectivity of protozoa.Infect Immun. 1998 Mar;66(3):883-92. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.3.883-892.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9488371 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory System Components as Potential Prophylactic Targets for Bacterial Pathogens.Biomolecules. 2021 Jun 15;11(6):892. doi: 10.3390/biom11060892. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34203937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
csrT Represents a New Class of csrA-Like Regulatory Genes Associated with Integrative Conjugative Elements of Legionella pneumophila.J Bacteriol. 2015 Nov 23;198(3):553-64. doi: 10.1128/JB.00732-15. Print 2016 Feb 1. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26598366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu Kwaik Y, Engleberg N C. Cloning and molecular characterization of a Legionella pneumophila gene induced by intracellular infection and by various in vitro stress stimuli. Mol Microbiol. 1994;13:243–251. - PubMed
-
- Abu Kwaik Y, Gao L, Harb O S, Stone B J. Transcriptional regulation of the macrophage-induced gene (gspA) of Legionella pneumophila and phenotypic characterization of a null mutant. Mol Microbiol. 1997;24:629–642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

