Granulocytic ehrlichiosis in tick-immune guinea pigs
- PMID: 9529119
- PMCID: PMC108126
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.4.1803-1805.1998
Granulocytic ehrlichiosis in tick-immune guinea pigs
Abstract
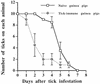
We investigated whether Ixodes scapularis-mediated host immunity interrupts transmission of the agent of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis (aoHGE) to guinea pigs. Ticks infected with aoHGE readily transmitted aoHGE to tick-immune guinea pigs, despite incomplete tick engorgement and host attachment. Although tick immunity can prevent Lyme borreliosis, protection is not afforded against granulocytic ehrlichiosis.
Figures

References
-
- Allen J R. Observation on the behavior of Dermacentor andersoni larvae infesting normal and tick resistant guinea pigs. Parasitology. 1982;84:195–204. - PubMed
-
- Bell J F, Stewart S J, Wikel S K. Resistance to tick-borne Francisella tularensis by tick sensitized rabbits: allergic klendusity. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1979;28:876–880. - PubMed
-
- Brossard M, Fivaz V. Ixodes ricinus L.: mast cells, basophils and eosinophils in the sequence of cellular events in the skin of infested or re-infested rabbits. Parasitology. 1982;85:583–592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

