Murine cytomegalovirus inhibits interferon gamma-induced antigen presentation to CD4 T cells by macrophages via regulation of expression of major histocompatibility complex class II-associated genes
- PMID: 9529320
- PMCID: PMC2212213
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.7.1037
Murine cytomegalovirus inhibits interferon gamma-induced antigen presentation to CD4 T cells by macrophages via regulation of expression of major histocompatibility complex class II-associated genes
Abstract
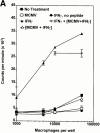
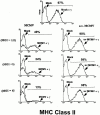
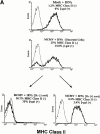
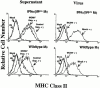
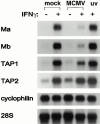
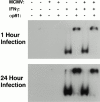
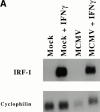
CD4 T cells and interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) are required for clearance of murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) infection from the salivary gland in a process taking weeks to months. To explain the inefficiency of salivary gland clearance we hypothesized that MCMV interferes with IFN-gamma induced antigen presentation to CD4 T cells. MCMV infection inhibited IFN-gamma-induced presentation of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II associated peptide antigen by differentiated bone marrow macrophages (BMMphis) to a T cell hybridoma via impairment of MHC class II cell surface expression. This effect was independent of IFN-alpha/beta induction by MCMV infection, and required direct infection of the BMMphis with live virus. Inhibition of MHC class II cell surface expression was associated with a six- to eightfold reduction in IFN-gamma induced IAb mRNA levels, and comparable decreases in IFN-gamma induced expression of invariant chain (Ii), H-2Ma, and H-2Mb mRNAs. Steady state levels of several constitutive host mRNAs, including beta-actin, cyclophilin, and CD45 were not significantly decreased by MCMV infection, ruling out a general effect of MCMV infection on mRNA levels. MCMV effects were specific to certain MHC genes since IFN-gamma-induced transporter associated with antigen presentation (TAP)2 mRNA levels were minimally altered in infected cells. Analysis of early upstream events in the IFN-gamma signaling pathway revealed that MCMV did not affect activation and nuclear translocation of STAT1alpha, and had minor effects on the early induction of IRF-1 mRNA and protein. We conclude that MCMV infection interferes with IFN-gamma-mediated induction of specific MHC genes and the Ii at a stage subsequent to STAT1alpha activation and nuclear translocation. This impairs antigen presentation to CD4 T cells, and may contribute to the capacity of MCMV to spread and persist within the infected host.
Figures




References
-
- Pavic I, Polic B, Crnkovic I, Lucin P, Jonjic S, Koszinowski UH. Participation of endogenous tumour necrosis factor-alpha in host resistance to cytomegalovirus infection. J Gen Virol. 1993;74:2215–2223. - PubMed
-
- Orange JS, Biron CA. Characterization of early IL-12, IFN-alpha/beta, and TNF effects on antiviral state and NK cell responses during murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Immunol. 1996;156:4746–4756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

