Ca2+ signaling modulates cytolytic T lymphocyte effector functions
- PMID: 9529322
- PMCID: PMC2212215
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.7.1057
Ca2+ signaling modulates cytolytic T lymphocyte effector functions
Abstract
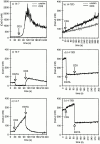
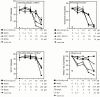
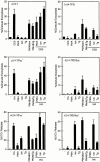
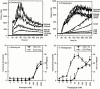
Cytolytic T cells use two mechanisms to kill virally infected cells, tumor cells, or other potentially autoreactive T cells in short-term in vitro assays. The perforin/granule exocytosis mechanism uses preformed cytolytic granules that are delivered to the target cell to induce apoptosis and eventual lysis. FasL/Fas (CD95 ligand/CD95)-mediated cytolysis requires de novo protein synthesis of FasL by the CTL and the presence of the death receptor Fas on the target cell to induce apoptosis. Using a CD8(+) CTL clone that kills via both the perforin/granule exocytosis and FasL/Fas mechanisms, and a clone that kills via the FasL/Fas mechanism only, we have examined the requirement of intra- and extracellular Ca2+ in TCR-triggered cytolytic effector function. These two clones, a panel of Ca2+ antagonists, and agonists were used to determine that a large biphasic increase in intracellular calcium concentration, characterized by release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores followed by a sustained influx of extracellular Ca2+, is required for perforin/granule exocytosis. Only the sustained influx of extracellular Ca2+ is required for FasL induction and killing. Thapsigargin, at low concentrations, induces this small but sustained increase in [Ca2+]i and selectively induces FasL/Fas-mediated cytolysis but not granule exocytosis. These results further define the role of Ca2+ in perforin and FasL/Fas killing and demonstrate that differential Ca2+ signaling can modulate T cell effector functions.
Figures
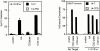
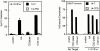


References
-
- Kagi D, Vignaux F, Ledermann B, Burki K, Depraetere V, Nagata S, Hengartner H, Golstein P. Fas and perforin pathways as major mechanisms of T cell–mediated cytotoxicity. Science. 1994;265:528–530. - PubMed
-
- Zheng L, Fisher G, Miller RE, Peschon J, Lynch DH, Lenardo MJ. Induction of apoptosis in mature T cells by tumour necrosis factor. Nature. 1995;377:348–351. - PubMed
-
- Kagi D, Hengartner H. Different roles for cytotoxic T cells in the control of infections with cytopathic versus noncytopathic viruses. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996;8:472–477. - PubMed
-
- Podack ER. Execution and suicide: cytotoxic lymphocytes enforce Draconian laws through separate molecular pathways. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995;7:11–16. - PubMed
-
- Clark WR, Walsh CM, Glass AA, Huang MT, Ahmed R, Matloubian M. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity in perforin-less mice. Int Rev Immunol. 1995;13:1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

