Molecular cloning of the cDNA encoding pp36, a tyrosine-phosphorylated adaptor protein selectively expressed by T cells and natural killer cells
- PMID: 9529333
- PMCID: PMC2212210
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.7.1157
Molecular cloning of the cDNA encoding pp36, a tyrosine-phosphorylated adaptor protein selectively expressed by T cells and natural killer cells
Abstract
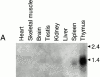
Activation of T and natural killer (NK) cells leads to the tyrosine phosphorylation of pp36 and to its association with several signaling molecules, including phospholipase Cgamma-1 and Grb2. Microsequencing of peptides derived from purified rat pp36 protein led to the cloning, in rat and man, of cDNA encoding a T- and NK cell-specific protein with several putative Src homology 2 domain-binding motifs. A rabbit antiserum directed against a peptide sequence from the cloned rat molecule recognized tyrosine phosphorylated pp36 from pervanadate-treated rat thymocytes. When expressed in 293T human fibroblast cells and tyrosine-phosphorylated, pp36 associated with phospholipase Cgamma-1 and Grb2. Studies with GST-Grb2 fusion proteins demonstrated that the association was specific for the Src homology 2 domain of Grb-2. Molecular cloning of the gene encoding pp36 should facilitate studies examining the role of this adaptor protein in proximal signaling events during T and NK cell activation.
Figures


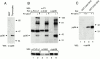

References
-
- Pawson T. Protein modules and signaling networks. Nature. 1995;373:573–580. - PubMed
-
- Chan AC, Desai DM, Weiss A. The role of protein tyrosine kinases and protein tyrosine phosphatases in T cell antigen receptor signal transduction. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:555–592. - PubMed
-
- Koretzky GA. The role of Grb-2–associated proteins in T-cell activation. Immunol Today. 1997;18:401–406. - PubMed
-
- Buday L, Egan SE, Viciana PR, Cantrell DA, Downward J. A complex of grb2 adaptor protein, sos exchange factor, and a 36-kDa membrane-bound tyrosine phosphoprotein is implicated in ras activation in T cells. J Biol Chem. 1993;269:9019–9023. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

