Arp2/3 complex from Acanthamoeba binds profilin and cross-links actin filaments
- PMID: 9529382
- PMCID: PMC25311
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.9.4.841
Arp2/3 complex from Acanthamoeba binds profilin and cross-links actin filaments
Abstract
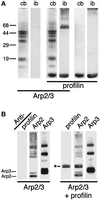
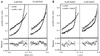
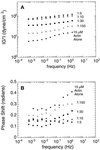
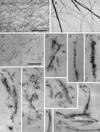
The Arp2/3 complex was first purified from Acanthamoeba castellanii by profilin affinity chromatography. The mechanism of interaction with profilin was unknown but was hypothesized to be mediated by either Arp2 or Arp3. Here we show that the Arp2 subunit of the complex can be chemically cross-linked to the actin-binding site of profilin. By analytical ultracentrifugation, rhodamine-labeled profilin binds Arp2/3 complex with a Kd of 7 microM, an affinity intermediate between the low affinity of profilin for barbed ends of actin filaments and its high affinity for actin monomers. These data suggest the barbed end of Arp2 is exposed, but Arp2 and Arp3 are not packed together in the complex exactly like two actin monomers in a filament. Arp2/3 complex also cross-links actin filaments into small bundles and isotropic networks, which are mechanically stiffer than solutions of actin filaments alone. Arp2/3 complex is concentrated at the leading edge of motile Acanthamoeba, and its localization is distinct from that of alpha-actinin, another filament cross-linking protein. Based on localization and actin filament nucleation and cross-linking activities, we propose a role for Arp2/3 in determining the structure of the actin filament network at the leading edge of motile cells.
Figures

References
-
- Bubb MR, Lewis MS, Korn ED. Actobindin binds with high affinity to a covalently cross-linked actin dimer. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:25587–25591. - PubMed
-
- Cooper JA, Pollard TD. Effects of capping protein on the kinetics of actin polymerization. Biochemistry. 1985;24:793–799. - PubMed
-
- Ferry JD. Viscoelestic Properties of Polymers. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley and Sons; 1980.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

