The thrombospondin receptor CD47 (IAP) modulates and associates with alpha2 beta1 integrin in vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 9529384
- PMCID: PMC25313
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.9.4.865
The thrombospondin receptor CD47 (IAP) modulates and associates with alpha2 beta1 integrin in vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
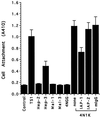
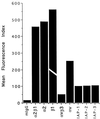
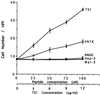
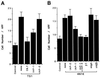
The carboxyl-terminal domain of thrombospondin-1 enhances the migration and proliferation of smooth muscle cells. Integrin-associated protein (IAP or CD47) is a receptor for the thrombospondin-1 carboxyl-terminal cell-binding domain and binds the agonist peptide 4N1K (kRFYVVMWKk) from this domain. 4N1K peptide stimulates chemotaxis of both human and rat aortic smooth muscle cells on gelatin-coated filters. The migration on gelatin is specifically blocked by monoclonal antibodies against IAP and a beta1 integrin, rather than alphav beta3 as found previously for 4N1K-stimulated chemotaxis of endothelial cells on gelatin. Both human and rat smooth muscle cells displayed a weak migratory response to soluble type I collagen; however, the presence of 4N1K peptide or intact thrombospondin-1 provoked a synergistic chemotactic response that was partially blocked by antibodies to alpha2 and beta1 integrin subunits and to IAP. A combination of antialpha2 and IAP monoclonal antibodies completely blocked chemotaxis. RGD peptide and antialphav beta3 mAb were without effect. 4N1K and thrombospondin-1 did not augment the chemotactic response of smooth muscle cells to fibronectin, vitronectin, or collagenase-digested type I collagen. Complex formation between alpha2 beta1 and IAP was detected by the coimmunoprecipitation of both alpha2 and beta1 integrin subunits with IAP. These data suggest that IAP can associate with alpha2 beta1 integrin and modulate its function.
Figures

References
-
- Abedi H, Dawes KE, Zachary I. Differential effects of platelet-derived growth factor BB on p125 focal adhesion kinase and paxillin tyrosine phosphorylation and on cell migration in rabbit aortic vascular smooth muscle cells and Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:11367–11376. - PubMed
-
- Adams JC, Tucker RP, Lawler J. The Thrombospondin Gene Family. Austin, TX: R.G. Landes Company; 1995.
-
- Asch AS, Silbiger S, Heimer E, Nachman RL. Thrombospondin sequence motif (CSVTCG) is responsible for CD 36 binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992;182:1208–1217. - PubMed
-
- Asch AS. The role of CD 36 as thrombospondin-1 receptor. In: Lahav J, editor. Thrombospondin. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1993. pp. 265–275.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

