Synthesis, storage, and release of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor (VEGF/VPF) by human mast cells: implications for the biological significance of VEGF206
- PMID: 9529385
- PMCID: PMC25314
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.9.4.875
Synthesis, storage, and release of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor (VEGF/VPF) by human mast cells: implications for the biological significance of VEGF206
Abstract
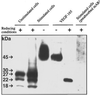
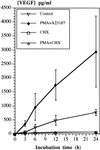
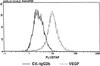
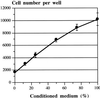
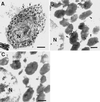
Mast cells have been implicated in various diseases that are accompanied by neovascularization. The exact mechanisms by which mast cells might mediate an angiogenic response, however, are unclear and therefore, we have investigated the possible expression of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor (VEGF/VPF) in the human mast cell line HMC-1 and in human skin mast cells. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis revealed that mast cells constitutively express VEGF121, VEGF165, and VEGF189. After a prolonged stimulation of cells for 24 h with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and the ionophore A23187, an additional transcript representing VEGF206 was detectable, as could be verified by sequence analysis. These results were confirmed at the protein level by Western blot analysis. When the amounts of VEGF released under unstimulated and stimulated conditions were compared, a significant increase was detectable after stimulation of cells. Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVEC) responded to the supernatant of unstimulated HMC-1 cells with a dose-dependent mitogenic effect, neutralizable up to 90% in the presence of a VEGF-specific monoclonal antibody. Flow cytometry and postembedding immunoelectron microscopy were used to detect VEGF in its cell-associated form. VEGF was exclusively detectable in the secretory granules of isolated human skin mast cells. These results show that both normal and leukemic human mast cells constitutively express bioactive VEGF. Furthermore, this study contributes to the understanding of the physiological role of the strongly heparin-binding VEGF isoforms, since these were found for the first time to be expressed in an activation-dependent manner in HMC-1 cells.
Figures

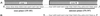

References
-
- Bacic M, Edwards NA, Merrill MJ. Differential expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (vascular permeability factor) forms in rat tissue. Growth Factor. 1995;12:11–15. - PubMed
-
- Butterfield JH, Weiler D, Dewald G, Gleich G, Gleich GJ. Establishment of an immature mast cell line from a patient with mast cell leukemia. Leuk Res. 1988;12:345–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

