Molecular genetics of mating recognition in basidiomycete fungi
- PMID: 9529887
- PMCID: PMC98906
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.62.1.55-70.1998
Molecular genetics of mating recognition in basidiomycete fungi
Abstract
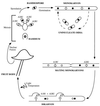
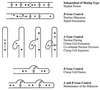
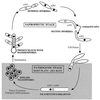
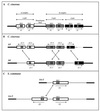
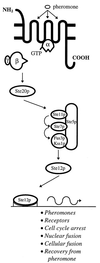
The recognition of compatible mating partners in the basidiomycete fungi requires the coordinated activities of two gene complexes defined as the mating-type genes. One complex encodes members of the homeobox family of transcription factors, which heterodimerize on mating to generate an active transcription regulator. The other complex encodes peptide pheromones and 7-transmembrane receptors that permit intercellular signalling. Remarkably, a single species may have many thousands of cross-compatible mating types because the mating-type genes are multiallelic. Different alleles of both sets of genes are necessary for mating compatibility, and they trigger the initial stages of sexual development--the formation of a specialized filamentous mycelium termed the dikaryon, in which the haploid nuclei remain closely associated in each cell but do not fuse. Three species have been taken as models to describe the molecular structure and organization of the mating-type loci and the genes sequestered within them: the pathogenic smut fungus Ustilago maydis and the mushrooms Coprinus cinereus and Schizophyllum commune. Topics addressed in this review are the roles of the mating-type gene products in regulating sexual development, the molecular basis for multiple mating types, and the molecular interactions that permit different allelic products of the mating type genes to be discriminated. Attention is drawn to the remarkable conservation in the mechanisms that regulate sexual development in basidiomycetes and unicellular ascomycete yeasts, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe, a theme which is developed in the general conclusion to include the filamentous ascomycetes Neurospora crassa and Podospora anserina.
Figures



References
-
- Aono T, Yanai H, Miki F, Davey J, Shimoda C. Mating pheromone-induced expression of the mat1-Pm gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe: identification of signalling components and characterization of upstream controlling elements. Yeast. 1994;10:757–770. - PubMed
-
- Asante-Owusu R N, Banham A H, Böhnert H U, Mellor E J C, Casselton L A. Heterodimerization between two classes of homeodomain proteins in the mushroom Coprinus cinereus brings together potential DNA-binding and activation domains. Gene. 1996;172:25–31. - PubMed
-
- Banham A H, Asante-Owusu R N, Göttgens B, Thompson S A J, Kingsnorth C S, Mellor E J C, Casselton L A. An N-terminal dimerization domain permits homeodomain proteins to choose compatible partners and initiate sexual development in the mushroom Coprinus cinereus. Plant Cell. 1995;7:773–783. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

