Cell wall and secreted proteins of Candida albicans: identification, function, and expression
- PMID: 9529890
- PMCID: PMC98909
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.62.1.130-180.1998
Cell wall and secreted proteins of Candida albicans: identification, function, and expression
Abstract
The cell wall is essential to nearly every aspect of the biology and pathogenicity of Candida albicans. Although it was initially considered an almost inert cellular structure that protected the protoplast against osmotic offense, more recent studies have demonstrated that it is a dynamic organelle. The major components of the cell wall are glucan and chitin, which are associated with structural rigidity, and mannoproteins. The protein component, including both mannoprotein and nonmannoproteins, comprises some 40 or more moieties. Wall proteins may differ in their expression, secretion, or topological location within the wall structure. Proteins may be modified by glycosylation (primarily addition of mannose residues), phosphorylation, and ubiquitination. Among the secreted enzymes are those that are postulated to have substrates within the cell wall and those that find substrates in the extracellular environment. Cell wall proteins have been implicated in adhesion to host tissues and ligands. Fibrinogen, complement fragments, and several extracellular matrix components are among the host proteins bound by cell wall proteins. Proteins related to the hsp70 and hsp90 families of conserved stress proteins and some glycolytic enzyme proteins are also found in the cell wall, apparently as bona fide components. In addition, the expression of some proteins is associated with the morphological growth form of the fungus and may play a role in morphogenesis. Finally, surface mannoproteins are strong immunogens that trigger and modulate the host immune response during candidiasis.
Figures
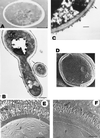

 ) appear to be more heavily concentrated in the inner cell wall domains; β-glucan–chitin complexes that appear to be formed by glycosidic linkages between both polymers will be located adjacent to the plasma membrane (PM) and the periplasmic space (ps). Proteins and glyco(manno)proteins (gp) appear to be dominant in the outermost cell wall layer, although they are also distributed through the entire wall structure. Once secreted through the plasma membrane, some protein and glycoproteins species will remain at the periplasmic space, possibly playing enzymatic roles (▵); some others will establish functional (i.e., β-glucanases [▾]) or structural covalent associations with β-glucans and possibly also with chitin (•—•) adjacent to the plasma membrane; and, finally, other moieties will constitute the most external layer, where the different molecular entities may be homogeneously (□) or heterogeneously (fimbriae, cluster of receptor-like molecules, etc. [○]) distributed or specifically released (i.e., extracellular enzymes) to the extracellular medium (EM) (•, ▪). Proteins and glycoprotein species in the outermost wall layer (□, ○) may establish different types of covalent (disulfide linkages) and noncovalent (hydrophobic and hydrogen ionic bonds) interactions. During their passage through the wall from the plasma membrane and periplasmic space to the outermost cell wall layers (□, ○) and possibly the extracellular environment (•, ▪), proteins and glycoproteins are most likely to be in equilibrium with other proteinaceous constituents, thus contributing, at least from a functional point of view, to the cell wall layering. In any case, protein and glycoprotein species other than those specifically secreted to the exocellular medium may also be released to such locations by dying (lysed) cells or as a consequence of unbalanced processes of synthesis and degradation of the cell wall structure, required for wall expansion during cell growth. To simplify the scheme, some aspects such as possible interactions of cell wall components with the plasma membrane and proteins retained in the cell wall, apparently by either covalent or noncovalent linkages, are not depicted.
) appear to be more heavily concentrated in the inner cell wall domains; β-glucan–chitin complexes that appear to be formed by glycosidic linkages between both polymers will be located adjacent to the plasma membrane (PM) and the periplasmic space (ps). Proteins and glyco(manno)proteins (gp) appear to be dominant in the outermost cell wall layer, although they are also distributed through the entire wall structure. Once secreted through the plasma membrane, some protein and glycoproteins species will remain at the periplasmic space, possibly playing enzymatic roles (▵); some others will establish functional (i.e., β-glucanases [▾]) or structural covalent associations with β-glucans and possibly also with chitin (•—•) adjacent to the plasma membrane; and, finally, other moieties will constitute the most external layer, where the different molecular entities may be homogeneously (□) or heterogeneously (fimbriae, cluster of receptor-like molecules, etc. [○]) distributed or specifically released (i.e., extracellular enzymes) to the extracellular medium (EM) (•, ▪). Proteins and glycoprotein species in the outermost wall layer (□, ○) may establish different types of covalent (disulfide linkages) and noncovalent (hydrophobic and hydrogen ionic bonds) interactions. During their passage through the wall from the plasma membrane and periplasmic space to the outermost cell wall layers (□, ○) and possibly the extracellular environment (•, ▪), proteins and glycoproteins are most likely to be in equilibrium with other proteinaceous constituents, thus contributing, at least from a functional point of view, to the cell wall layering. In any case, protein and glycoprotein species other than those specifically secreted to the exocellular medium may also be released to such locations by dying (lysed) cells or as a consequence of unbalanced processes of synthesis and degradation of the cell wall structure, required for wall expansion during cell growth. To simplify the scheme, some aspects such as possible interactions of cell wall components with the plasma membrane and proteins retained in the cell wall, apparently by either covalent or noncovalent linkages, are not depicted.References
-
- Aguiar J M, Baquero F, Jones J M. Candida albicans exocellular antigens released into a synthetic culture medium: characterization and serological response in rabbits. J Gen Microbiol. 1993;139:3005–3010. - PubMed
-
- Akashi T, Homma M, Kanbe T, Tanaka K. Ultrastructure of proteinase-secreting cells of Candida albicans studied by alkaline bismuth staining and immunocytochemistry. J Gen Microbiol. 1993;139:2185–2195. - PubMed
-
- Alloush H M, López-Ribot J L, Chaffin W L. Dynamic expression of cell wall proteins of Candida albicans revealed by probes from cDNA clones. J Med Vet Mycol. 1996;34:91–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

