General and cancer specific mortality of a population based cohort of patients with inflammatory bowel disease: the Florence Study
- PMID: 9536940
- PMCID: PMC1726997
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.42.2.175
General and cancer specific mortality of a population based cohort of patients with inflammatory bowel disease: the Florence Study
Abstract
Background: A population based epidemiological study identified all the patients diagnosed with ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn's disease (CD) resident in the Florence area in the period 1978-1992.
Aims: To assess the mortality of unselected patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in a Mediterranean country.
Methods: Overall, 920 patients (689 UC and 231 CD) were followed until death or end of follow up (31 December 1996). Information on vital status was available for all except eight patients (0.9%); 70 deaths were identified (23 in patients with CD and 47 in patients with UC). Expected deaths were estimated on the basis of five year age group, gender, and calendar year national mortality rates. Standardised mortality ratios (SMR) and 95% confidence intervals were calculated.
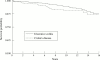
Results: General mortality was significantly lower than expected in UC (SMR 0.6; 95% confidence interval 0.4 to 0.8), due to a reduced number of cardiovascular and, possibly, smoking related deaths. Cancers of the respiratory tract were significantly reduced in UC but tended to be increased in patients with CD. These latter patients had not only an increased cancer mortality but also a 40% increased risk of dying for all causes already evident in the first five year follow up period and persisting thereafter. In contrast, in patients with UC, SMRs were initially very low but tended to increase steadily over the follow up period. Gastrointestinal deaths were particularly increased in patients with CD, but only moderately in those with UC. Overall, there was some evidence of a twofold increased mortality for colorectal cancer, the risk being highest for rectal cancers in patients with UC. A non-significant excess of deaths due to haemolymphopoietic malignancies and suicides was also observed.
Conclusions: This study, the first in a Mediterranean country, supports the existence of two divergent mortality patterns for patients with UC and CD, possibly explained by differences in smoking habits and by a greater severity of CD.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical