Amiodarone and the thyroid: a practical guide to the management of thyroid dysfunction induced by amiodarone therapy
- PMID: 9538302
- PMCID: PMC1728611
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.79.2.121
Amiodarone and the thyroid: a practical guide to the management of thyroid dysfunction induced by amiodarone therapy
Abstract
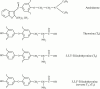
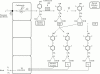
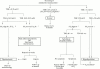
Amiodarone induces predictable changes in thyroid function tests that are largely explicable in terms of the physiological effects of iodide excess and inhibition of deiodinase activity. Clinically relevant thyroid dysfunction is not uncommon during amiodarone therapy, and requires careful diagnosis and treatment. The diagnosis and management of thyrotoxicosis is probably best supervised by a specialist endocrinologist. Control of hypothyroidism can generally be achieved simply by the addition of T4 to the therapeutic regimen, ideally after an initial assessment by an endocrinologist. The frequency with which amiodarone causes thyroid and other complications serves to emphasize the need for rational prescribing and long-term cardiological follow up.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
