The human U5-200kD DEXH-box protein unwinds U4/U6 RNA duplices in vitro
- PMID: 9539711
- PMCID: PMC22463
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.8.4188
The human U5-200kD DEXH-box protein unwinds U4/U6 RNA duplices in vitro
Abstract
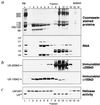
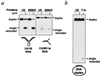
Splicing of nuclear precursors of mRNA (pre-mRNA) involves dynamic interactions between the RNA constituents of the spliceosome. The rearrangement of RNA-RNA interactions, such as the unwinding of the U4/U6 duplex, is believed to be driven by ATP-dependent RNA helicases. We recently have shown that spliceosomal U5 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) from HeLa cells contain two proteins, U5-200kD and U5-100kD, which share homology with the DEAD/DEXH-box families of RNA helicases. Here we demonstrate that purified U5 snRNPs exhibit ATP-dependent unwinding of U4/U6 RNA duplices in vitro. To identify the protein responsible for this activity, U5 snRNPs were depleted of a subset of proteins under high salt concentrations and assayed for RNA unwinding. The activity was retained in U5 snRNPs that contain the U5-200kD protein but lack U5-100kD, suggesting that the U5-200kD protein could mediate U4/U6 duplex unwinding. Finally, U5-200kD was purified to homogeneity by glycerol gradient centrifugation of U5 snRNP proteins in the presence of sodium thiocyanate, followed by ion exchange chromatography. The RNA unwinding activity was found to reside exclusively with the U5-200kD DEXH-box protein. Our data raise the interesting possibility that this RNA helicase catalyzes unwinding of the U4/U6 RNA duplex in the spliceosome.
Figures



References
-
- Moore M J, Query C C, Sharp P A. In: The RNA World. Gesteland R F, Atkins J F, editors. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 1993. pp. 303–357.
-
- Will C L, Lührmann R. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997;9:320–327. - PubMed
-
- Nilsen T W. Cell. 1994;78:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Madhani H D, Guthrie C. Annu Rev Genet. 1994;28:1–26. - PubMed
-
- Konforti B B, Koziolkiewicz M J, Konarska M M. Cell. 1993;75:863–873. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

