DnaA-stimulated transcriptional activation of orilambda: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase beta subunit as a transcriptional activator contact site
- PMID: 9539721
- PMCID: PMC22473
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.8.4241
DnaA-stimulated transcriptional activation of orilambda: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase beta subunit as a transcriptional activator contact site
Abstract
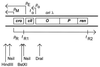
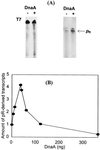
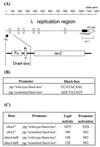
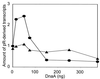
We present evidence that Escherichia coli RNA polymerase beta subunit may be a transcriptional activator contact site. Stimulation of the activity of the pR promoter by DnaA protein is necessary for replication of plasmids derived from bacteriophage lambda. We found that DnaA activates the pR promoter in vitro. Particular mutations in the rpoB gene were able to suppress negative effects that certain dnaA mutations had on the replication of lambda plasmids; this suppression was allele-specific. When a potential DnaA-binding sequence located several base pairs downstream of the pR promoter was scrambled by in vitro mutagenesis, the pR promoter was no longer activated by DnaA both in vivo and in vitro. Therefore, we conclude that DnaA may contact the beta subunit of RNA polymerase during activation of the pR promoter. A new classification of prokaryotic transcriptional activators is proposed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The mechanism of regulation of bacteriophage lambda pR promoter activity by Escherichia coli DnaA protein.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jun 20;278(25):22250-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M212492200. Epub 2003 Mar 24. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12654908
-
Escherichia coli dnaA gene function and bacteriophage lambda replication.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1998 Oct 1;167(1):27-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1998.tb13203.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1998. PMID: 9785448
-
The double mechanism of incompatibility between lambda plasmids and Escherichia coli dnaA(ts) host cells.Microbiology (Reading). 2001 Jul;147(Pt 7):1923-1928. doi: 10.1099/00221287-147-7-1923. Microbiology (Reading). 2001. PMID: 11429468
-
Stimulation of the phage lambda pL promoter by integration host factor requires the carboxy terminus of the alpha-subunit of RNA polymerase.J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):985-90. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90514-k. J Mol Biol. 1992. PMID: 1433303 Review.
-
A model for initiation at origins of DNA replication.Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):915-8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90102-x. Cell. 1988. PMID: 2843291 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional Activity of the Bacterial Replication Initiator DnaA.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 1;12:662317. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.662317. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34140937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replicating DNA by cell factories: roles of central carbon metabolism and transcription in the control of DNA replication in microbes, and implications for understanding this process in human cells.Microb Cell Fact. 2013 May 29;12:55. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-12-55. Microb Cell Fact. 2013. PMID: 23714207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of physiological regulation of RNA synthesis in bacteria: new discoveries breaking old schemes.J Appl Genet. 2007;48(3):281-94. doi: 10.1007/BF03195225. J Appl Genet. 2007. PMID: 17666783 Review.
-
Composition of the lambda plasmid heritable replication complex.Biochem J. 2002 Jun 15;364(Pt 3):857-62. doi: 10.1042/BJ20011488. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12049651 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial regulation of genes essential for Myxococcus xanthus development involves a response regulator and a LysR-type regulator.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 May 8;104(19):7969-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701569104. Epub 2007 Apr 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17470804 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

