DnaA-stimulated transcriptional activation of orilambda: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase beta subunit as a transcriptional activator contact site
- PMID: 9539721
- PMCID: PMC22473
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.8.4241
DnaA-stimulated transcriptional activation of orilambda: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase beta subunit as a transcriptional activator contact site
Abstract
We present evidence that Escherichia coli RNA polymerase beta subunit may be a transcriptional activator contact site. Stimulation of the activity of the pR promoter by DnaA protein is necessary for replication of plasmids derived from bacteriophage lambda. We found that DnaA activates the pR promoter in vitro. Particular mutations in the rpoB gene were able to suppress negative effects that certain dnaA mutations had on the replication of lambda plasmids; this suppression was allele-specific. When a potential DnaA-binding sequence located several base pairs downstream of the pR promoter was scrambled by in vitro mutagenesis, the pR promoter was no longer activated by DnaA both in vivo and in vitro. Therefore, we conclude that DnaA may contact the beta subunit of RNA polymerase during activation of the pR promoter. A new classification of prokaryotic transcriptional activators is proposed.
Figures
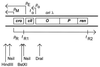
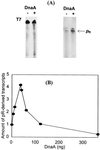
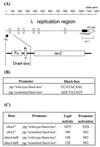
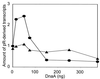
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

