PCR for detection of Shigella spp. in mayonnaise
- PMID: 9546158
- PMCID: PMC106136
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.64.4.1242-1245.1998
PCR for detection of Shigella spp. in mayonnaise
Abstract
The use of PCR to amplify a specific virA gene fragment serves as a highly specific and sensitive method to detect virulent bacteria of the genus Shigella and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Amplification of a 215-bp DNA band was obtained by using isolated genomic DNA of Shigella, individual cells of Shigella dysenteriae, and mayonnaise contaminated with S. dysenteriae. Moreover, a multiplex PCR with specific (virA) and bacterium-restricted (16S ribosomal DNA) primers generated an amplification product of approximately 755 bp for all bacteria tested and an additional 215-bp product for Shigella and enteroinvasive E. coli.
Figures
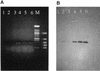
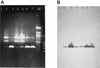
References
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J D, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1994. pp. 2.4.1–2.4.5.
-
- Batt C A. Molecular diagnostic for dairy-borne pathogens. J Dairy Sci. 1997;80:220–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

