A novel sensitive bioassay for detection of Bacillus cereus emetic toxin and related depsipeptide ionophores
- PMID: 9546170
- PMCID: PMC106152
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.64.4.1338-1343.1998
A novel sensitive bioassay for detection of Bacillus cereus emetic toxin and related depsipeptide ionophores
Abstract
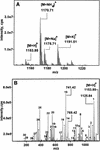
Of the toxins produced by Bacillus cereus, the emetic toxin is likely the most dangerous but, due to the lack of a suitable assay, the least well known. In this paper, a new, sensitive, inexpensive, and rapid bioassay for detection of the emetic toxin of B. cereus is described. The assay is based on the loss of motility of boar spermatozoa upon 24 h of exposure to extracts of emetic B. cereus strains or contaminated food. The paralyzed spermatozoa exhibited swollen mitochondria, but no depletion of cellular ATP or damage to plasma membrane integrity was observed. Analysis of the purified toxin by electrospray tandem mass spectrometry showed that it was a dodecadepsipeptide with a mass fragmentation pattern similar to that described for cereulide. The 50% effective concentration of the purified toxin to boar spermatozoa was 0.5 ng of purified toxin ml of extended boar semen-1. This amount corresponds to 10(4) to 10(5) CFU of B. cereus cells. No toxicity was detected for 27 other B. cereus strains up to 10(8) CFU ml-1. The detection limit for food was 3 g of rice containing 10(6) to 10(7) CFU of emetic B. cereus per gram. Effects similar to those provoked by emetic B. cereus toxin were also induced in boar spermatozoa by valinomycin and gramicidin at 2 and 3 ng ml of extended boar semen-1, respectively. The symptoms provoked by the toxin in spermatozoa indicated that B. cereus emetic toxin was acting as a membrane channel-forming ionophore, damaging mitochondria and blocking the oxidative phosphorylation required for the motility of boar spermatozoa.
Figures
References
-
- Agata N, Mori M, Ohta M, Suwan S, Ohtani I, Isobe M. A novel dodecadepsipeptide, cereulide, isolated from Bacillus cereus causes vacuole formation in HEp-2 cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1994;121:31–34. - PubMed
-
- Agata N, Ohta M, Masashi M, Isobe M. A novel dodecadepsipeptide, cereulide, is an emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1995;129:17–20. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama N, Mitani K, Tanaka Y, Hanazono Y, Motoi N, Zarcovic M, Tange T, Hirai H, Yazaki Y. Fulminant septicemic syndrome of Bacillus cereus in a leukemic patient. Intern Med. 1997;36:221–227. - PubMed
-
- Andersson M, Katila T. The Hague Congress proceedings 4. The 12th International Congress in Animal Reproduction, The Hague, The Netherlands, 23 to 27 August 1992. 1992. Evaluation of frozen-thawed stallion semen with a motility analyzer; pp. 1837–1839.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

