Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 present in radish sprouts
- PMID: 9546189
- PMCID: PMC106182
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.64.4.1532-1535.1998
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 present in radish sprouts
Abstract
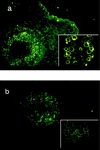
Using cultivation, immunofluorescence microscopy, and scanning electron microscopy, we demonstrated the presence of viable enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 not only on the outer surfaces but also in the inner tissues and stomata of cotyledons of radish sprouts grown from seeds experimentally contaminated with the bacterium. HgCl2 treatment of the outer surface of the hypocotyl did not kill the contaminating bacteria, which emphasized the importance of either using seeds free from E. coli O157:H7 in the production of radish sprouts or heating the sprouts before they are eaten.
Figures

References
-
- Andrews W H, Mislivec P B, Wilson C R, Bruce V R, Poelma P L, Gibson R, Trucksess M W, Young K. Microbial hazards associated with bean sprouting. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1982;65:241–248. - PubMed
-
- Beuchat L R. Comparison of chemical treatment to kill salmonella on alfalfa seeds destined for sprout production. Int J Food Microbiol. 1997;34:329–333. - PubMed
-
- Como-Sabetti K, Reagan S, Allaire S, Parrott K, Simonds C M, Hrabowy S, Ritter B, Hall W, Altamirano J, Martin R, Downes F, Jennings G, Barrie R, Dorman M F, Keon N, Kucab M, Al Shab A, Robinson-Dunn B, Dietrich S, Moshur L, Reese L, Smith J, Wilcox K, Tilden J, Wojtala G, Park J D, Winnett M, Petrilack L, Vasquez L, Jenkins S, Barrett E, Linn M, Woolard D, Hackler R, Martin H, McWilliams D, Rouse B, Willis S, Rullan J, Miller G, Jr, Henderson S, Pearson J, Beers J, Davis R, Saunders D Food-Borne and Diarrheal Diseases Branch, Division of Bacterial and Mycotic Diseases, National Center for Infectious Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreaks of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection associated with eating alfalfa sprouts—Michigan and Virginia, June-July 1997. Morbid Mortal Weekly Rep. 1997;46:741–744.
-
- Hara-Kudo Y, Konuma H, Iwaki M, Kasuga F, Sugita-Konishi Y, Ito Y, Kumagai S. Potential hazard of radish sprouts as a vehicle of Escherichia coli O157:H7. J Food Prot. 1997;60:1125–1127. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

