CD40 ligand is not essential for induction of type 1 cytokine responses or protective immunity after primary or secondary infection with histoplasma capsulatum
- PMID: 9547342
- PMCID: PMC2212226
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.8.1315
CD40 ligand is not essential for induction of type 1 cytokine responses or protective immunity after primary or secondary infection with histoplasma capsulatum
Abstract
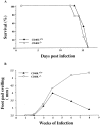
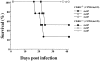
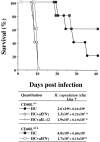
The induction of type 1 immune responses (interleukin [IL]-12, interferon [IFN]-gamma) has been shown to be important in mediating protection against many intracellular infections including Histoplasma capsulatum. Costimulatory molecules such as CD40 ligand (CD40L) have been shown to be a central regulator of type 1 responses in vivo. To study the role of CD40L in mediating protection against infection with H. capsulatum, CD40L-deficient (CD40L-/-) and CD40L+/+ mice were infected with H. capsulatum and assessed for various parameters. After a lethal challenge of H. capsulatum, CD40L-/- mice were not substantially different from CD40L+/+ mice in terms of mortality, fungal burden, or production of IFN-gamma, IL-12, nitric oxide, or tumor necrosis factor alpha. Moreover, CD40L-/- mice treated with anti-IFN-gamma or anti-IL-12 at the time of infection had accelerated mortality, providing further evidence that IL-12 and IFN-gamma are produced in vivo in the absence of CD40L. In addition, CD40L-/- mice infected with a sublethal dose of H. capsulatum survived infection, whereas all mice infected with the same dose and treated with anti-IFN-gamma had accelerated mortality, demonstrating that IFN-gamma but not CD40L was essential for primary immunity to H. capsulatum infection. Interestingly, depletion of either CD4+ or CD8+ T cells resulted in accelerated mortality in CD40L-/- mice, suggesting a critical role for these cells in response to infection. Finally, CD40L-/- mice initially infected with a sublethal dose of H. capsulatum were protected from secondary infection with a lethal dose of H. capsulatum, demonstrating that CD40L is not required for the maintenance of memory immunity.
Figures




References
-
- Grewal IS, Xu J, Flavell RA. Impairment of antigen-specific T cell priming in mice lacking CD40 ligand. Nature. 1995;348:617–620. - PubMed
-
- McDyer JF, Goletz TJ, Thomas E, June CH, Seder RA. CD40 ligand/CD40 stimulation regulates the production of IFN-γ from human PBMCs in an IL-12– and/ or CD28–dependent manner. J Immunol. 1998;160:1701–1707. - PubMed
-
- Shu U, Kiniwa M, Wu CY, Maliszewski C, Vezzio N, Hakimi J, Gately M, Delespesse G. Activated T cells induced interleukin-12 production by monocytes via CD40–CD40 ligand interaction. Eur J Immunol. 1995;25:1125–1128. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

