Role of domain I of neuronal Ca2+ channel alpha1 subunits in G protein modulation
- PMID: 9547390
- PMCID: PMC2230935
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.163bo.x
Role of domain I of neuronal Ca2+ channel alpha1 subunits in G protein modulation
Abstract
1. We studied the G protein inhibition of heteromultimeric neuronal Ca2+ channels by constructing a series of chimeric channels between the strongly modulated alpha1B subunit and the alpha1E(rbEII) subunit, which showed no modulation. 2. In parallel studies, alpha1 subunit constructs were co-expressed together with the accessory Ca2+ channel alpha2-delta and beta2a subunits in mammalian (COS-7) cells and Xenopus oocytes. G protein inhibition of expressed Ca2+ channel currents was induced by co-transfection of Gbeta1 and Ggamma2 subunits in COS-7 cells or activation of co-expressed dopamine (D2) receptors by quinpirole (100 nM) in oocytes. 3. The data indicate that transfer of the alpha1B region containing the N-terminal, domain I and the I-II loop (i.e. the alpha1B1-483 sequence), conferred G protein modulation on alpha1E(rbEII), both in terms of a slowing of activation kinetics and a reduction in current amplitude. 4. In contrast, the data are not consistent with the I-II loop and/or the C-terminal forming a unique site for G protein modulation.
Figures


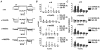
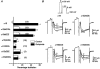
References
-
- Campbell V, Berrow N, Brickley K, Page K, Wade R, Dolphin AC. Voltage-dependent calcium channel β-subunits in combination with alpha1 subunits have a GTPase activating effect to promote hydrolysis of GTP by G alphao in rat frontal cortex. FEBS Letters. 1995;370:135–140. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, DeVivo M, Dingus J, Harry A, Li J, Sui J, Carty DJ, Blank JL, Exton JH, Stoffel RH, Inglese J, Lefkowitz RJ, Logothetis DE, Hildebrandt JD, Iyengar R. A region of adenylyl cyclase 2 critical for regulation by G protein beta gamma subunits. Science. 1995;268:1166–1169. - PubMed
-
- De Waard M, Liu H, Walker D, Scott VE, Gurnett CA, Campbell KP. Direct binding of G-protein βγ complex to voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1997;385:446–450. 10.1038/385446a0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

