Human autoantibodies reveal titin as a chromosomal protein
- PMID: 9548712
- PMCID: PMC2148454
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.141.2.321
Human autoantibodies reveal titin as a chromosomal protein
Abstract
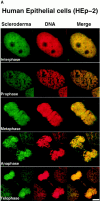
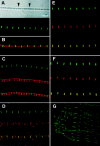
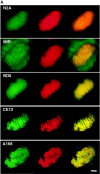
Assembly of the higher-order structure of mitotic chromosomes is a prerequisite for proper chromosome condensation, segregation and integrity. Understanding the details of this process has been limited because very few proteins involved in the assembly of chromosome structure have been discovered. Using a human autoimmune scleroderma serum that identifies a chromosomal protein in human cells and Drosophila embryos, we cloned the corresponding Drosophila gene that encodes the homologue of vertebrate titin based on protein size, sequence similarity, developmental expression and subcellular localization. Titin is a giant sarcomeric protein responsible for the elasticity of striated muscle that may also function as a molecular scaffold for myofibrillar assembly. Molecular analysis and immunostaining with antibodies to multiple titin epitopes indicates that the chromosomal and muscle forms of titin may vary in their NH2 termini. The identification of titin as a chromosomal component provides a molecular basis for chromosome structure and elasticity.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

