p21 is a critical CDK2 regulator essential for proliferation control in Rb-deficient cells
- PMID: 9548727
- PMCID: PMC2148461
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.141.2.503
p21 is a critical CDK2 regulator essential for proliferation control in Rb-deficient cells
Abstract
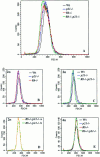
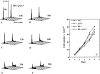
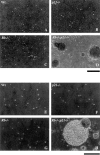
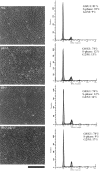
Proliferation in mammalian cells is controlled primarily in the G1-phase of the cell cycle through the action of the G1 cyclin-dependent kinases, CDK4 and CDK2. To explore the mechanism of cellular response to extrinsic factors, specific loss of function mutations were generated in two negative regulators of G1 progression, p21 and pRB. Individually, these mutations were shown to have significant effects in G1 regulation, and when combined, Rb and p21 mutations caused more profound defects in G1. Moreover, cells deficient for pRB and p21 were uniquely capable of anchorage-independent growth. In contrast, combined absence of pRB and p21 function was not sufficient to overcome contact inhibition of growth nor for tumor formation in nude mice. Finally, animals with the genotype Rb+/-;p21(-/-) succumbed to tumors more rapidly than Rb+/- mice, suggesting that in certain contexts mutations in these two cell cycle regulators can cooperate in tumor development.
Figures




References
-
- Baldin V, Lukas J, Marcote MJ, Pagano M, Draetta J. Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for progression in G1. Genes Dev. 1993;7:812–821. - PubMed
-
- Brugarolas J, Chandrasekaran C, Gordon JI, Beach D, Jacks T, Hannon GJ. Radiation-induced cell cycle arrest compromised by p21 deficiency. Nature. 1995;377:552–557. - PubMed
-
- Chellappan SP, Hiebert S, Mudryj M, Horowitz JM, Nevins JR. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 1991;65:1053–1061. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

