Isolation and characterization of methanophenazine and function of phenazines in membrane-bound electron transport of Methanosarcina mazei Gö1
- PMID: 9555882
- PMCID: PMC107126
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.8.2027-2032.1998
Isolation and characterization of methanophenazine and function of phenazines in membrane-bound electron transport of Methanosarcina mazei Gö1
Abstract
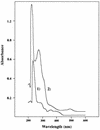
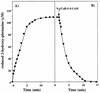
A hydrophobic, redox-active component with a molecular mass of 538 Da was isolated from lyophilized membranes of Methanosarcina mazei Gö1 by extraction with isooctane. After purification on a high-performance liquid chromatography column, the chemical structure was analyzed by mass spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance studies. The component was called methanophenazine and represents a 2-hydroxyphenazine derivative which is connected via an ether bridge to a polyisoprenoid side chain. Since methanophenazine was almost insoluble in aqueous buffers, water-soluble phenazine derivatives were tested for their ability to interact with membrane-bound enzymes involved in electron transport and energy conservation. The purified F42OH2 dehydrogenase from M. mazei Gö1 showed highest activity with 2-hydroxyphenazine and 2-bromophenazine as electron acceptors when F420H2 was added. Phenazine-1-carboxylic acid and phenazine proved to be less effective. The Km values for 2-hydroxyphenazine and phenazine were 35 and 250 microM, respectively. 2-Hydroxyphenazine was also reduced by molecular hydrogen catalyzed by an F420-nonreactive hydrogenase which is present in washed membrane preparations. Furthermore, the membrane-bound heterodisulfide reductase was able to use reduced 2-hydroxyphenazine as an electron donor for the reduction of CoB-S-S-CoM. Considering all these results, it is reasonable to assume that methanophenazine plays an important role in vivo in membrane-bound electron transport of M. mazei Gö1.
Figures



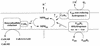
References
-
- Abken H J, Deppenmeier U. Purification and properties of an F420H2 dehydrogenase from Methanosarcina mazei Gö1. FEMS Lett. 1997;154:231–237.
-
- Daniels L, Sparling R, Sprott G D. The bioenergetics of methanogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984;768:113–163. - PubMed
-
- Deppenmeier U, Blaut M, Gottschalk G. Dependence on membrane components of methanogenesis from methyl-CoM with formaldehyde or molecular hydrogen as electron donors. Eur J Biochem. 1989;186:317–323. - PubMed
-
- Deppenmeier U, Blaut M, Gottschalk G. H2:heterodisulfide oxidoreductase, a second energy-conserving system in the methanogenic strain Gö1. Arch Microbiol. 1991;155:272–277.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

