Inorganic polyphosphate in Escherichia coli: the phosphate regulon and the stringent response
- PMID: 9555903
- PMCID: PMC107147
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.8.2186-2193.1998
Inorganic polyphosphate in Escherichia coli: the phosphate regulon and the stringent response
Abstract
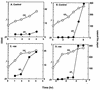
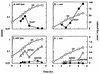
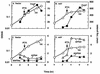
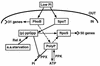
Escherichia coli transiently accumulates large amounts of inorganic polyphosphate (polyP), up to 20 mM in phosphate residues (Pi), in media deficient in both Pi and amino acids. This transient accumulation is preceded by the appearance of nucleotides ppGpp and pppGpp, generated in response to nutritional stresses. Mutants which lack PhoB, the response regulator of the phosphate regulon, do not accumulate polyP even though they develop wild-type levels of (p)ppGpp when subjected to amino acid starvation. When complemented with a phoB-containing plasmid, phoB mutants regain the ability to accumulate polyP. PolyP accumulation requires high levels of (p)ppGpp independent of whether they are generated by RelA (active during the stringent response) or SpoT (expressed during Pi starvation). Hence, accumulation of polyP requires a functional phoB gene and elevated levels of (p)ppGpp. A rapid assay of polyP depends on its adsorption to an anion-exchange disk on which it is hydrolyzed by a yeast exopolyphosphatase.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Guanosine tetra- and pentaphosphate promote accumulation of inorganic polyphosphate in Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 22;272(34):21240-3. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.34.21240. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9261133
-
Inorganic Polyphosphate Accumulation in Escherichia coli Is Regulated by DksA but Not by (p)ppGpp.J Bacteriol. 2019 Apr 9;201(9):e00664-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00664-18. Print 2019 May 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30745375 Free PMC article.
-
Inorganic polyphosphate and the stringent response coordinately control cell division and cell morphology in Escherichia coli.mBio. 2025 Feb 5;16(2):e0351124. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03511-24. Epub 2024 Dec 27. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39727417 Free PMC article.
-
Inorganic polyphosphate regulates responses of Escherichia coli to nutritional stringencies, environmental stresses and survival in the stationary phase.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 1999;23:183-95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-58444-2_9. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10448677 Review.
-
[The stringent response--bacterial mechanism of an adaptive stress response].Postepy Biochem. 2006;52(1):87-93. Postepy Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16869306 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Extraction and Quantification of Poly P, Poly P Analysis by Urea-PAGE.Bio Protoc. 2014 May 5;4(9):e1113. doi: 10.21769/bioprotoc.1113. Bio Protoc. 2014. PMID: 27453910 Free PMC article.
-
At the Crossroad of Nucleotide Dynamics and Protein Synthesis in Bacteria.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2023 Mar 21;87(1):e0004422. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00044-22. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36853029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyphosphate Dynamics in Cable Bacteria.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 19;13:883807. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.883807. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35663875 Free PMC article.
-
Novel assay reveals multiple pathways regulating stress-induced accumulations of inorganic polyphosphate in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 1998 Apr;180(7):1841-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.7.1841-1847.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9537383 Free PMC article.
-
Inorganic polyphosphate and the stringent response coordinately control cell division and cell morphology in Escherichia coli.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 12:2024.09.11.612536. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.11.612536. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: mBio. 2025 Feb 05;16(2):e0351124. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03511-24. PMID: 39314361 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Akiyama M, Crooke E, Kornberg A. The polyphosphate kinase gene of Escherichia coli: isolation and sequence of the ppk gene and membrane location of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:22556–22561. - PubMed
-
- Bracha M, Yagil E. A new type of alkaline phosphatase-negative mutants in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1973;122:53–60. - PubMed
-
- Cashel M. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. IV. Relevance of unusual phosphorylated compounds from amino acid starved stringent strains. J Biol Chem. 1969;244:3133–3141. - PubMed
-
- Cashel M, Gentry D R, Hernandez V J, Vinella D. The stringent response. In: Neidhardt F C, Curtiss III R, Ingraham J L, Lin E C C, Low K B, Magasanik B, Reznikoff W S, Riley M, Schaechter M, Umbarger H E, editors. Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology. Washington, D.C: American Society for Microbiology; 1996. pp. 1458–1496.
-
- Castuma C E, Huang R, Kornberg A, Reusch R N. Inorganic polyphosphates in the acquisition of competence in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:12980–12983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

