Activation of caspases in pig kidney cells infected with wild-type and CrmA/SPI-2 mutants of cowpox and rabbitpox viruses
- PMID: 9557631
- PMCID: PMC109571
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.5.3524-3533.1998
Activation of caspases in pig kidney cells infected with wild-type and CrmA/SPI-2 mutants of cowpox and rabbitpox viruses
Abstract
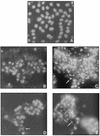
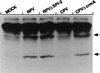
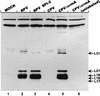
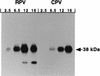
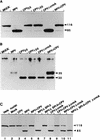
The cowpox virus (CPV) CrmA and the equivalent rabbitpox virus (RPV) SPI-2 proteins have anti-inflammatory and antiapoptosis activity by virtue of their ability to inhibit caspases, including the interleukin-1beta-converting enzyme (ICE; caspase-1). Infection of LLC-PK1 pig kidney cells with a CPV CrmA mutant, but not with wild-type (wt) CPV, results in the induction of many of the morphological features of apoptosis (C. A. Ray and D. J. Pickup, Virology 217:384-391, 1996). In our study, LLC-PK1 cells infected with CPV delta crmA, but not those infected with wt CPV, showed induction of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)- and lamin A-cleaving activities and processing of the CPP32 (caspase-3) precursor to a mature 18-kDa form. Surprisingly, infection of LLC-PK1 cells with either wt RPV (despite the presence of the SPI-2 protein) or RPV delta SPI-2 resulted in cleavage activity against PARP and lamin A and the appearance of the mature subunit of CPP32/caspase-3. The biotinylated specific peptide inhibitor Ac-Tyr-Val-Lys(biotinyl)-Asp-2,6-dimethylbenzoyloxymethylketone [AcYV(bio)KD-aomk] labeled active caspase subunits of 18, 19, and 21 kDa in extracts from LLC-PK1 cells infected with CPV delta crmA, wt RPV, or RPV delta SPI-2 but not wt CPV. Mixed infection of LLC-PK1 cells with wt RPV and wt CPV gave no PARP-cleaving activity, and all PARP cleavage mediated by SPI-2 and CrmA mutants of RPV and CPV, respectively, could be eliminated by coinfection with wt CPV. These results suggest that the RPV SPI-2 and CPV CrmA proteins are not functionally equivalent and that CrmA, but not SPI-2 protein, can completely prevent apoptosis in LLC-PK1 cells under these conditions.
Figures




References
-
- Alcami A, Smith G L. Cytokine receptors encoded by poxviruses: a lesson in cytokine biology. Immunol Today. 1995;16:474–478. - PubMed
-
- Alcami A, Smith G L. Soluble interferon-gamma receptors encoded by poxviruses. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1996;19:305–317. - PubMed
-
- Ali A N, Turner P C, Brooks M A, Moyer R W. The SPI-1 gene of rabbitpox virus determines host range and is required for hemorrhagic pock formation. Virology. 1994;202:306–314. - PubMed
-
- Alnemri E S, Livingston D J, Nicholson D W, Salvesen G, Thornberry N A, Wong W W, Yuan J. Human ICE/CED-3 protease nomenclature. Cell. 1996;87:171. - PubMed
-
- Boldin M P, Goncharov T M, Goltsev Y V, Wallach D. Involvement of MACH, a novel MORT1/FADD-interacting protease, in Fas/APO-1- and TNF receptor-induced cell death. Cell. 1996;85:803–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

