Cross-reactions between the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses of human immunodeficiency virus-infected African and European patients
- PMID: 9557634
- PMCID: PMC109574
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.5.3547-3553.1998
Cross-reactions between the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses of human immunodeficiency virus-infected African and European patients
Abstract
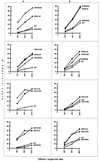
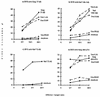
The great variability of protein sequences from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 (HIV-1) isolates represents a major obstacle to the development of an effective vaccine against this virus. The surface protein (Env), which is the predominant target of neutralizing antibodies, is particularly variable. Here we examine the impact of variability among different HIV-1 subtypes (clades) on cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) activities, the other major component of the antiviral immune response. CTLs are produced not only against Env but also against other structural proteins, as well as some regulatory proteins. The genetic subtypes of HIV-1 were determined for Env and Gag from several patients infected either in France or in Africa. The cross-reactivities of the CTLs were tested with target cells expressing selected proteins from HIV-1 isolates of clade A or B or from HIV type 2 isolates. All African patients were infected with viruses belonging to clade A for Env and for Gag, except for one patient who was infected with a clade A Env-clade G Gag recombinant virus. All patients infected in France were infected with clade B viruses. The CTL responses obtained from all the African and all the French individuals tested showed frequent cross-reactions with proteins of the heterologous clade. Epitopes conserved between the viruses of clades A and B appeared especially frequent in Gag p24, Gag p18, integrase, and the central region of Nef. Cross-reactivity also existed among Gag epitopes of clades A, B, and G, as shown by the results for the patient infected with the clade A Env-clade G Gag recombinant virus. These results show that CTLs raised against viral antigens from different clades are able to cross-react, emphasizing the possibility of obtaining cross-immunizations for this part of the immune response in vaccinated individuals.
Figures

References
-
- Ariyoshi K, Cham F, Berry N, Jaffar S, Sabally S, Corrah T, Whittle H. HIV-2-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity is inversely related to proviral load. AIDS. 1995;9:555–559. - PubMed
-
- Bolognesi D. HIV antibodies and vaccine design. AIDS. 1989;3:S111–S119. - PubMed
-
- Brander C, Walker B D. The HLA-class I-restricted CTL response in HIV-1 infection; identification of optimal epitopes. HIV Molecular Immunology Database. Los Alamos, N.Mex: Los Alamos National Laboratory; 1995. . IV-1 to IV-8.
-
- Buseyne F, Stevanovic S, Rammensee H-G, Rivière Y. Characterization of an HIV-1 p24gag epitope recognized by a CD8+ cytotoxic T-cell clone. Immunol Lett. 1997;55:145–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

