Interaction of poliovirus with its purified receptor and conformational alteration in the virion
- PMID: 9557638
- PMCID: PMC109578
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.5.3578-3586.1998
Interaction of poliovirus with its purified receptor and conformational alteration in the virion
Abstract
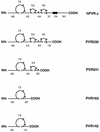
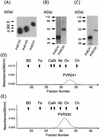
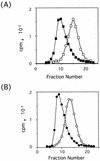
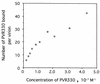
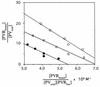
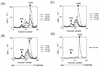
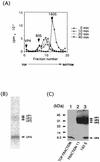
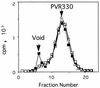
Polypeptides of amino acids 1 to 241 (PVR241) and 1 to 330 (PVR330) of the human poliovirus receptor (hPVR) were produced in a baculovirus expression system. PVR241 contained extracellular domains 1 and 2 of hPVR, and PVR330 contained extracellular domains 1, 2, and 3. These peptides were purified by immunoaffinity column chromatography with an anti-hPVR monoclonal antibody (MAb). After the purification, PVR241 and PVR330 appeared to retain their native conformation as judged by reactivity with an anti-PVR MAb that recognized domain 1 of hPVR in a conformation-dependent manner. The virulent Mahoney strain of poliovirus type 1 was mixed with the purified PVRs in various concentrations. An average of at least 43 PVR330 molecules were able to bind to one virion particle under the conditions used. The equilibrium dissociation constant between the PVR330 molecule and the PVR binding site (canyon) on the virion was determined to be 4.50 +/- (0.86) x 10(-8) M at 4 degrees C. Higher rates of conformational change of the virus (160S) to 135S and 80S particles were observed as the concentration of PVR330 was increased. In this in vitro system, the ratio of the amount of the 135S particle to that of the 80S particle seemed to be always constant. After the disappearance of the 160S particle, the amount of the 80S particle was not increased by further incubation at 37 degrees C. These results suggested that the 80S particle was not derived from the 135S particle under the conditions used in this study.
Figures
References
-
- Aoki J, Koike S, Asou H, Ise I, Suwa H, Tanaka T, Miyasaka M, Nomoto A. Mouse homolog of poliovirus receptor-related gene 2 product, mPRR2, mediates homophilic cell aggregation. Exp Cell Res. 1997;235:374–384. - PubMed
-
- Aoki J, Koike S, Ise I, Sato-Yoshida Y, Nomoto A. Amino acid residues on human poliovirus receptor involved in interaction with poliovirus. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:8431–8438. - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt G, Bibb J A, Bradley J, Wimmer E. Molecular characterization of the cellular receptor for poliovirus. Virology. 1994;199:105–113. - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt G, Harber J, Zibert A, deCrombrugghe M, Wimmer E. The poliovirus receptor: identification of domains and amino acid residues critical for virus binding. Virology. 1994;203:344–356. - PubMed
-
- Bibb J A, Bernhardt G, Wimmer E. Cleavage site of the poliovirus receptor signal sequence. J Gen Virol. 1994;75:1875–1881. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

