Collaboration of antibody and inflammation in clearance of rabies virus from the central nervous system
- PMID: 9557653
- PMCID: PMC109593
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.5.3711-3719.1998
Collaboration of antibody and inflammation in clearance of rabies virus from the central nervous system
Abstract
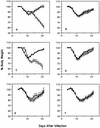
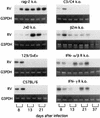
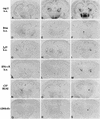
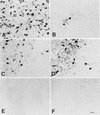
To investigate the involvement of various cellular and humoral aspects of immunity in the clearance of rabies virus from the central nervous system, (CNS), we studied the development of clinical signs and virus clearance from the CNS in knockout mice lacking either B and T cells, CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, B cells, alpha/beta interferon (IFN-alpha/beta) receptors, IFN-gamma receptors, or complement components C3 and C4. Following intranasal infection with the attenuated rabies virus CVS-F3, normal adult mice of different genetic backgrounds developed a transient disease characterized by loss of body weight and appetite depression which peaked at 13 days postinfection (p.i.). While these animals had completely recovered by day 21 p.i., mice lacking either B and T cells or B cells alone developed a progressive disease and succumbed to infection. Mice lacking either CD8+ T cells, IFN receptors, or complement components C3 and C4 showed no significant differences in the development of clinical signs by comparison with intact counterparts having the same genetic background. However, while infectious virus and viral RNA could be detected in normal control mice only until day 8 p.i., in all of the gene knockout mice studied except those lacking C3 and C4, virus infection persisted through day 21 p.i. Analysis of rabies virus-specific antibody production together with histological assessment of brain inflammation in infected animals revealed that clearance of CVS-F3 by 21 days p.i. correlated with both a strong inflammatory response in the CNS early in the infection (day 8 p.i.), and the rapid (day 10 p.i.) production of significant levels of virus-neutralizing antibody (VNA). These studies confirm that rabies VNA is an absolute requirement for clearance of an established rabies virus infection. However, for the latter to occur in a timely fashion, collaboration between VNA and inflammatory mechanisms is necessary.
Figures
References
-
- Davis D R, Metzger H. Structural basis of antibody function. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:87–117. - PubMed
-
- Dietzschold B, Schwaeble W, Schaeffer M K-H, Hooper D C, Zheng Y M, Petry F, Sheng H, Fink T, Loos M, Koprowski H, Weihe E. Expression of C1q, a subcomponent of the rat complement system, is dramatically enhanced in brains of rats with either Borna disease or experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neurol Sci. 1995;130:11–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

