Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum chaperones in the folding of hepatitis C virus glycoproteins
- PMID: 9557669
- PMCID: PMC109609
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.5.3851-3858.1998
Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum chaperones in the folding of hepatitis C virus glycoproteins
Abstract
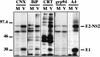
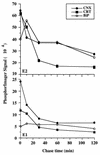
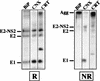
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) genome encodes two envelope glycoproteins (E1 and E2) which interact noncovalently to form a heterodimer (E1-E2). During the folding and assembly of HCV glycoproteins, a large portion of these proteins are trapped in aggregates, reducing the efficiency of native E1-E2 complex assembly. To better understand this phenomenon and to try to increase the efficiency of HCV glycoprotein folding, endoplasmic reticulum chaperones potentially interacting with these proteins were studied. Calnexin, calreticulin, and BiP were shown to interact with E1 and E2, whereas no interaction was detected between GRP94 and HCV glycoproteins. The association of HCV glycoproteins with calnexin and calreticulin was faster than with BiP, and the kinetics of interaction with calnexin and calreticulin were very similar. However, calreticulin and BiP interacted preferentially with aggregates whereas calnexin preferentially associated with monomeric forms of HCV glycoproteins or noncovalent complexes. Tunicamycin treatment inhibited the binding of HCV glycoproteins to calnexin and calreticulin, indicating the importance of N-linked oligosaccharides for these interactions. The effect of the co-overexpression of each chaperone on the folding of HCV glycoproteins was also analyzed. However, the levels of native E1-E2 complexes were not increased. Together, our data suggest that calnexin plays a role in the productive folding of HCV glycoproteins whereas calreticulin and BiP are probably involved in a nonproductive pathway of folding.
Figures
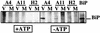
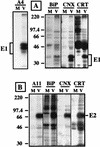
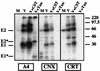
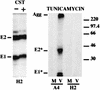

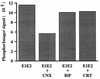
References
-
- Bergeron J J M, Brenner M B, Thomas D Y, Williams D B. Calnexin: a membrane-bound chaperone of the endoplasmic reticulum. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994;19:124–129. - PubMed
-
- Cannon K S, Hebert D N, Helenius A. Glycan-dependent and -independent association of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein with calnexin. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:14280–14284. - PubMed
-
- Chamberlain J P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979;98:132–135. - PubMed
-
- Choo Q-L, Kuo G, Weiner A J, Overby L R, Bradley D W, Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989;244:359–362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

