Overexpression, purification, and characterization of the cloned metallo-beta-lactamase L1 from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
- PMID: 9559809
- PMCID: PMC105568
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.4.921
Overexpression, purification, and characterization of the cloned metallo-beta-lactamase L1 from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
Abstract
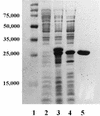
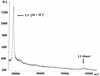
The metallo-beta-lactamase L1 from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia was cloned, overexpressed, and characterized by spectrometric and biochemical techniques. Results of metal analyses were consistent with the cloned enzyme having 2 mol of tightly bound Zn(II) per monomer. Gel filtration chromatography demonstrated that the cloned enzyme exists as a tightly held tetramer with a molecular mass of ca. 115 kDa, and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization and time-of-flight mass spectrometry indicated a monomeric molecular mass of 28.8 kDa. Steady-state kinetic studies with a number of diverse penicillin and cephalosporin antibiotics demonstrated that L1 effectively hydrolyzes all tested compounds, with k(cat)/Km values ranging between 0.002 and 5.5 microM(-1) s(-1). These characteristics of the recombinant enzyme are contrasted to those previously reported for metallo-beta-lactamases isolated directly from S. maltophilia.
Figures
References
-
- Bandoh K, Watanabe K, Muto Y, Tanaka Y, Kato N, Ueno K. Conjugal transfer of imipenem resistance in Bacteriodes fragilis. J Antibiot. 1992;45:542–547. - PubMed
-
- Concha N O, Rasmussen B A, Bush K, Herzberg O. Crystal structure of the wide-spectrum binuclear zinc β-lactamase from Bacteroides fragilis. Structure. 1996;4:823–836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

